The consumer drone market is expected to grow up to $3.26 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9% according to The business research company. More and more people are discovering how useful and valuable these drones can be in their day-to-day lives.
Today we’re going to explain everything you should know about consumer drones.
So, what are consumer drones?
Consumer drones, often referred to as hobby or personal drones, are unmanned aerial systems (UAS) that are manufactured for drone hobbyists/recreational drone pilots. There are many different types of consumer drones such as multi-rotor, fixed-wing, or toy drones. Consumer drones are primarily used for photography and videography.
Before we go into detail about consumer drones, let’s quickly clear up a common mistake people often make. By this we are talking about confusing consumer drones with commercial drones.
- Consumer And Commercial Drones
- What Are The Main Types Of Consumer Drones?
- What Are Consumer Drones Used For
- Consumer Drone Market Size
- Consumer Drone Sizes
- What Materials Are Drones Made Of?
- What Are The Main Parts Of A Consumer Drone?
- How Fast Can Consumer Drones Fly?
- How Much Are Consumer Drones?
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Drones
- Consumer Drone Abilities
- Examples Of Consumer Drones
- Conclusion
Consumer And Commercial Drones
Consumer and commercial drones are not actually the same.
Consumer drones, as mentioned above, are drones designed specifically for recreational purposes, meaning without the intention to use the drone to make money.
Commercial drones are drones that were made for specific jobs. These drones find applications in various industries such as the agriculture, energy, oil, and even the filmmaking industry to name a few.
These types of drones are usually more expensive as they are of a higher quality build, be it the materials and design of the frame, purpose-built software or high-tech equipment which together contribute to a more efficient execution of tasks for the commercial operation.
If you’d like to read more on this topic, we have a full post on some drone pilot jobs that you could get:
Related Post: 5 Amazing Drone Pilot Jobs You Can Get Today
What Are The Main Types Of Consumer Drones?
There are several different types of consumer drones on the market today. These drones are all different in some way whether that be how they look or how they function.
Here are all the different types of drones.
Rotary blade drones
There are two categories when it comes to rotary blade drones. One being multi-rotor drones, and the other single rotor drones.
Multi-rotor drones
Multi-rotor drones can be classified into several types: tricopters, quadcopters, hexacopters and octocopters.
Tricopters are drones that have three propellers. These types of drones are often more efficient than drones with more propellers as they have less of everything.
These drones are often very cheap as they do not have as many components as the other drones we’ll discuss below.
Quadcopters are the types of drones most people know as they are the main drones being produced for the consumer market. They have four propellers and there are a wide variety of models that vary in price.
Quadcopters range from $30-$2,000 and the range of quality depends on their price.
Hexacopters are drones with six propellers. Octocopters have eight propellers. These drones are often very expensive as they are made with high-quality materials. They have a wide range of uses such as taking professional photos and videos and carrying very heavy payloads.
These drones can cost anywhere from $1,000 to over $16,000.
However, there are some beginner-level drones of these types that can cost between $100 and $400.
Single rotor drones
Single rotor drones resemble helicopters. They are often called RC helicopters and are more efficient than multi-rotor drones.
These drones have one large primary propeller while a second smaller propeller at the tail of the drone prevents the drone from spinning.
Fixed-wing drones
Fixed-wing drones resemble planes or gliders and are capable of flying for much longer than rotary blade drones because of their gliding capabilities.
It can be challenging to learn to fly fixed-wing drones at first. Some require a runway to take off, some can take off vertically and others need a person to throw the drone for it to fly.
Prices range from $50 up to $300. They usually have very large wingspans and have various weights.
Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) hybrid drones
VTOL drones are capable of taking off vertically and switching to a horizontal flight mode by slowly tilting the propellers towards the nose of the vehicle. These drones are becoming more and more popular as they are very efficient because of their fixed wings, and are capable of taking off without a runway.
These drones however are mostly very expensive with prices up to $20,000 and up for the high quality drones such as the WingtraOne. Below is a short video of the WingtraOne VTOL drone in action!
Underwater drone/Remotely operated vehicle (ROV)
Underwater drones/ROVs are drones that are capable of diving deep into the depth of the ocean. These drones can cost you from a few hundred to thousands of dollars depending on size and capabilities.
Here is a short video of the popular Geneinno Titan ROV in action:
There are two types of ROVs, tethered and wireless.
Tethered ROVs are underwater drones that have a cable that attaches to a buoy or boat in order for the drone not to get lost and to allow the drone to relay things such as video footage in real-time.
Wireless drones have the same capabilities but cannot go nearly as deep in order to prevent losing connection to the drone.
If you’d like to find out a little on how deep underwater ROVs can go, whether this be consumer drones or professional drones not available to the public, then check out our post on this topic here:
Related Post: How Deep Can Underwater Drones Go? Guide To ROV Depth Capabilities
Toy drones
For the sake of length, we’re going to combine nano and mini drones with toy drones as many mini drones were made to be toys for children and novice drone pilots.
These drones are widely available and are usually cheap with prices that range from $10 to $250. These drones are compact.
Nano drones are considered to be the smallest types of drones in the world. To give you an idea, they are smaller than your palm.
Mini drones are larger than nano drones but are just a little larger than your hand. These drones have a lot more functions and sensors and are also usually more expensive.
These drones are often used indoors but some mini drones are designed for outdoor use as well. The lower quality drones can range from $30 to $70 whereas the higher quality ones can cost $300 and up.
If you’d like to find out whether you can fly your drone indoors, whether you have a drone made to be used indoors, the reasons for why you may want to do so, whether it’s legal, the different types of indoor drones and much more, then check out our detailed post below:
Related Post: Indoor Drone Flying: Everything You Need To Know
Some nano and mini drones are being used by the military and also have some professional applications.
Racing drones
Racing drones is a very cool activity that’s widely becoming known by many. It’s incredible to watch people who have mastered the first person view (FPV) by looking through goggles going at speeds exceeding 100 mph (161 km/h).
These drones are often very expensive and require custom builds in order to achieve the speeds mentioned above.
Drones like these start around $500 but can easily break the $1000 mark if you’re aiming to exceed 100 mph (161 km/h).
There are many racing drones currently available on the market but most cannot exceed 50 mph (80km/h).
If you’d like to learn more on all kinds of drone speeds for different types of drones, check out our detailed post below:
Related Post: How Fast Can A Drone Fly? An In-Depth Guide To Drone Anatomy
Here is a link to the drone racing league’s website if you’d like to learn more on this sport:
The Drone Racing League | The Premier Drone Racing League.
What Are Consumer Drones Used For
Consumer drones are mainly used as toys, for racing or for photography and videography.
Beginner drone pilots who are trying to learn how to fly a drone start off with toy drones to get the hang of it. This includes kids who are just trying to have fun.
Professional drone racers compete in very fast-paced races in large indoor areas with many obstacles to overcome to win that first place position.
Whoever can build the fastest, lightest drone gains an edge on the competition.
The main application for a consumer drone is photography and videography. Most drones are built to be stable and well balanced, equipped, or capable of being equipped with high definition cameras, and with stable recording during flight enabled by camera gimbles.
These camera drones range from mini drones to large professional drones with prices ranging from $300 all the way up to $14,000 depending on how serious you take your passion.
Consumer Drone Market Size
With an increasing demand for consumer drones for aerial photography and first person view (FPV) racing, the Federal Aviation Association (FAA) has had trouble adding new laws and regulations on drones fast enough in order to ensure that they are being used safely and legally.
This is due to the incredibly rapid growth drones have seen in recent years.
North America consumer drone market by technology, 2012 – 2022 (USD Million):
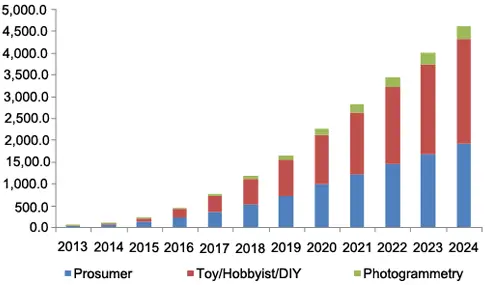
As the graph above shows, there has been a considerable growth in the drone industry since 2013.
Toy/hobbyist applications segment is expected to witness considerable growth, growing at a CAGR of close to 35% from 2016 to 2024.
Grand view research
This research was done back in 2016 and the numbers may have changed. Let’s look at research conducted in 2021.
According to research done by The Business Research Company:
The global consumer drones market is expected grow from $2.09 billion in 2020 to $2.34 billion in 2021 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%.
The Business Research Company
This global consumer drone market is expected to reach $3.26 billion in 2025, leading back to the 9% CAGR over the six-year period. Aerial photography is the leading use of drones by recreational pilots and is the leading factor that impacts these numbers.
Hobbyist drones are expected to triple from 1.1 million units in 2016 to 3.5 million in 2021.
These are some incredible findings and show the potential this industry has.
Consumer Drone Sizes
There are many sizes for consumer drones. These range from very small drones to large drones. These sizes often influence the quality and price of the drone.
Let’s get into some of these consumer drone sizes.
Disclaimer: The below drone sizes are for consumer drones and do not include military UAVs
Very small drones
Very small drones can weigh as little as 11 grams. These drones can fit comfortably in your hand and can even be transported in your pocket!
The current Guinness World Record for the world’s smallest drone is the Hubsan H111 NANO Q4 weighing 11.5 grams (0.0115kg).
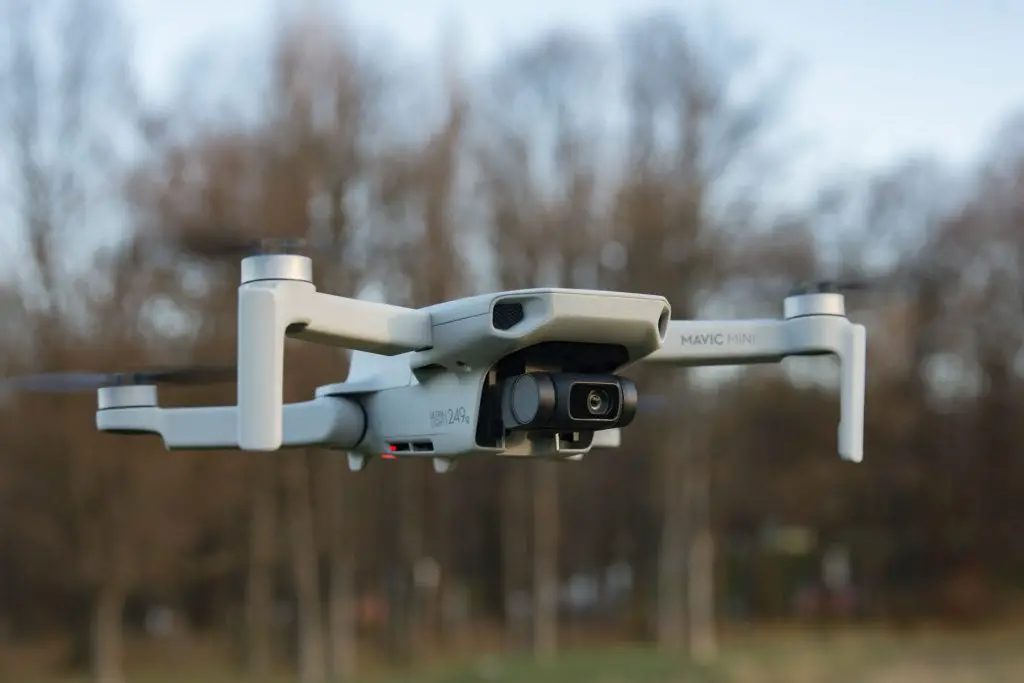
Small drones
Small drones are usually in the 200-300 grams range. These drones are typically a little larger than your hand but can still easily and comfortably rest on it.
One popular example is the DJI Mavic Mini which weighs 249 grams (0.249 kg).

Medium-size drones
Medium size drones usually weigh between 1,000 to 5,000 grams (1-5 kg). These drones, as you might have guessed, can no longer comfortably rest in the palm of your hand as they are considerably larger and heavier than small-sized drones.
A popular example of a medium-size drone is the DJI Phantom 4 Pro which weighs 1388 grams (1,388 kg)
Large drones
Large drones can weigh anywhere from 2 kg to 10 kg (2,000 to 10000 grams) and up. These drones are meant to be very durable and resistant.
They are fairly large in size and begin to become quite difficult to carry with one person.
They are often fixed-wing types of drones but are also multi-rotor drones as well sold by companies such as DJI.
An example would be the DJI Spreading Wings S900 which weighs 3.3 kg (3,300 grams) without equipment. Here is a short video on it below:
What Materials Are Drones Made Of?
Many drones use alloys to build their frames as some combinations of metals can create even stronger and lighter metals.
Many drones use magnesium and aluminum alloys while others use titanium, carbon fiber and even thermoplastics.
Drones usually use combinations of these metals and alloys on different parts of their drones as some materials are better suited for different parts.
We have a full post that goes into detail about the materials commonly used in all types of drones today and each of their components below (including some examples):
Related Post: What Are Drones Made Of? Detailed Guide To Drone Anatomy [Consumer+Commercial]
What Are The Main Parts Of A Consumer Drone?
Most drones are built with specific intentions in mind, whether that be for speed, flight duration, durability or stability.
Understanding a drone’s components can get you one step closer to building, maintaining or simply buying the perfect drone.
Here are the main parts of a consumer drone:
- The Frame
- Flight Controller: Controls every instruction given by the drone pilot
- Motors
- Propellers
- Batteries
- GPS Module: The global positioning satellite module finds the longitude, latitude and elevation points
- Electronic Speed Controller (ESC): Monitors and changes the speed of the drone, changes the direction of flight and converts DC battery power to AC battery power so that the motors can function
- LED Lights
- Power Distribution Board: Monitors the amount of power given from the battery to distribute to the ESC and flight controller
- 3 Axis Gimbal: Keeps the camera mounted on the drone stable
- Camera
- Transmitter: Transmits radio signals from the drone’s controller to the drone itself so that the operator can control the drone
- Receiver: Receives radio waves from transmitter and is found in the drone
For a more detailed guide on the parts and the materials that make up consumer and commercial drones, check out this post below:
Related Post: What Are Drones Made Of? Detailed Guide To Drone Anatomy [Consumer+Commercial]
How Fast Can Consumer Drones Fly?
As drone technology evolves, so does the top speed of a drone. Consumer drones are becoming faster while still being capable of obtaining stable, high quality footage and an overall fun experience.
Rotary blade consumer drones on average are capable of obtaining speeds of 40-70mph (64-113km/h).
Rotary blade toy drones can reach an average of 12mph (19km/h).
Rotary blade racing drones can reach average speeds of over 130mph (209km/h).
Fixed-wing drones can reach average speeds of 30-50mph (48-80km/h).
If you’d like to learn more on what impacts the top speeds of drones, the legal drone speed limit and more on drone speeds, check out our post below:
Related Post: How Fast Can A Drone Fly? An In-Depth Guide To Drone Anatomy
How Much Are Consumer Drones?
Consumer drones range in price depending on many factors such as the quality of the drone and the drone’s abilities.
Some drone’s are capable of doing a lot more than others. Some drones have a lot more features such as additional sensors.
Here are different price ranges of cheap and expensive drones.
Consumer drones that are considered cheap fall under the price range of between $30-$200.
Consumer drones that are considered expensive fall under the price range of $300 and up. These drones can cost as much as $14,000.
Check out our post on cheap vs expensive drones where we go into how good cheap and expensive drones are, how hard and long they can fly and the main differences between the two:
Related Post: Cheap VS Expensive Drones – Everything A Beginner Drone Pilot Should Know
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Drones
Their are many advantages and disadvantages to drones. Although they may have many benefits, these awesome devices are not perfect, yet.
Here is a short list of some advantages and disadvantages of drones.
Advantages:
- The number one advantage of course is that they’re fun!
- They’re cheaper then manned aircrafts
- They can get you beautiful aerial footage
- They can reach areas you otherwise couldn’t
- They can provide security from the skies
Disadvantages:
- You can be easily accused of spying if you fly your drone in a neighbourhood
- They have short flight times, limited by battery capacity, weight and range
- Some lack avoidance sensors, so pilot error can lead them into collision with obstacles and other objects
- They can get you into legal trouble if you fly too near to restricted areas
- Drones are easily affected by bad weather
Consumer Drone Abilities
By ‘abilities’ we are referring to certain technologies that drones may have implemented in their systems such as GPS that have enabled them to fly for longer, deliver packages and even do tricks.
Here’s a really cool video showcasing a drone doing front flips, barrel rolls and other cool tricks:
Here are a few abilities drones can have.
Ready to fly (RTF) drones
RTF drones are drones that come with a full assembly kit in a box for you to quickly and easily assemble and start using your drone.
GPS drones
These types of drones are linked to satellites in order to determine their exact location. This can enable the awesome ‘Return to home’ function some drones have.
Trick drones
Trick drones are usually classed in the toy drone category. They’re small and maneuverable and are capable of quickly doing barrel rolls and flips, but do not have very advanced technology other than this.
Endurance drones
Endurance drones are drones that have been optimised to stay in the air for hours, and sometimes days if we’re including military drones. These drones have big batteries and are as light as possible to reduce the battery consumption.
Fixed-wing drones are more suited to be endurance drones as they have the added benefit of being able to glide long distances and therefore reduce the amount it needs to use its battery.
Alternative powered drones
These drones are being powered with alternative methods other than electricity. For example, gasoline, nitro-fuel and solar.
Nitro-fuel (often called RC glow fuel) is primarily used for RC cars that are trying to achieve high speeds as nitromethane boosts power output.
Solar-powered fixed-wing drones are starting to make appearances in the world of drones.
These drones have solar panels on their winged areas to capture the sun rays and recharge themselves while flying allowing for long flight times (Airbus Zephyr).
Examples Of Consumer Drones
Most drones can be used for commercial purposes. It’s as easy as selling footage you got from your drone. However, we will only be including drones that were primarily built for recreational pilots or people trying to capture beautiful aerial footage.
Here are 10 popular consumer drones (This list is not ordered in any way):
- DJI Mini 2
- DJI Mavic Pro
- DJI Inspire 2
- Parrot Anafi
- Ryze Tello
- DJI Mavic 2 Pro
- DJI Air 2S
- Parrot Disco
- Yuneec Typhoon H Plus
- DJI Spark
Conclusion
Consumer drones are just beginning their rise to the top. People are constantly finding new applications for these drones and discovering the specific benefits they have in the racing and photography industries.
We hope you enjoyed this post and learned something new about consumer drones!
