Image 1 Source– By Spanish Coches; Image 2 Source – By RobSimmons223311; Image 3 Source; Image 4 Source
Unmanned trucks/lorries, also called robotic trucks or truck unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) are quickly gaining in popularity as the new age of autonomous vehicles (specifically fully autonomous) comes within our grasp.
Various companies have been developing and testing semi to fully autonomous trucks, some small companies and others that are very large (more on this below).
Unmanned trucks, also called robotic trucks are types of powered drones/unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) that are designed to carry and transport freight (cargo) or specialised payloads.
Robotic trucks range in size from small toy-grade trucks you can pick up to large scale trucks that are the size of real manned vehicles used to haul cargo.
Take note that unmanned trucks include remote-control (RC)/teleoperated, autonomous/self-driving, and artificially intelligent unmanned trucks.
These types of unmanned vehicles fall under the broad category of unmanned motor vehicles. Unmanned motor vehicles are sub-types of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs).
How Do Unmanned Trucks Work?
Unmanned truck drones/robots propel themselves using a power source and several rotating wheels along with a suspension, steering, braking and communications system enabling them to be controlled remotely and/or semi to fully autonomous.
Truck UGVs experience several forces including thrust generated by a power source that opposes drag caused by air resistance and friction generated by the moving mechanical parts such as spinning wheels against the axles.
Their various parts and components work in unison enabling the vehicle to function such as a chassis, body, wheels, power sources, suspension systems etc. (more on this below).
Pitch, roll, and yaw are each present in moving robotic trucks and can be controlled to a degree by the suspension system.
Pitch is the change in angle of an unmanned truck along its transverse axis forwards and backwards. When the front of the truck goes up, the back goes down and vice versa.
Roll, also called body roll, is the change in angle of the body of an unmanned truck along its longitudinal axis. If a person stood at one side of the truck (passenger or driver’s side) and lifted it somehow, that would be a roll.
Yaw is the change in angle of an unmanned truck along its vertical axis. When the truck turns, it changes direction either going left or right. This is called yaw and is different from roll as all the wheels stay on the ground.
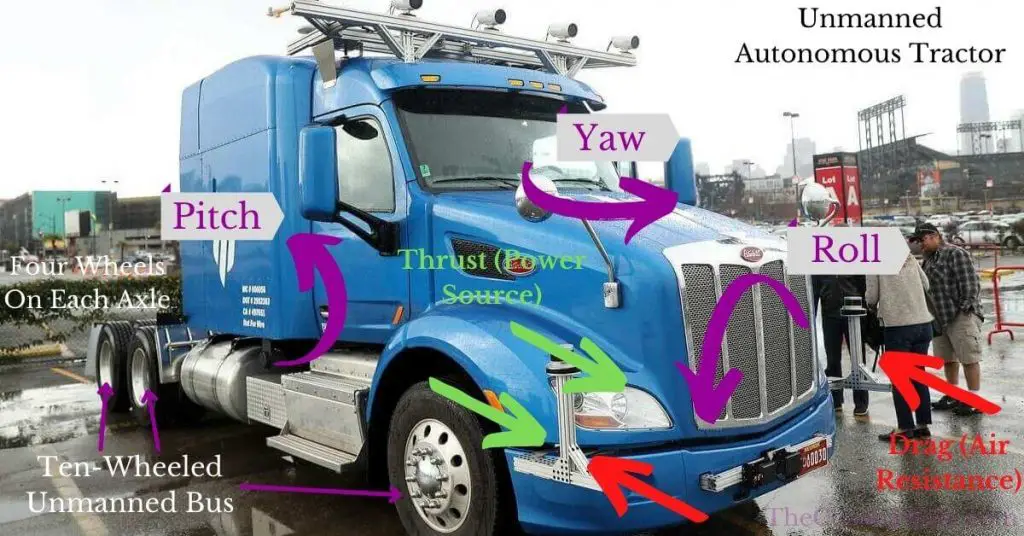
Understanding and monitoring the pitch, roll, and yaw control of an unmanned truck is important as each of them slightly changes the truck’s centre of gravity causing a weight transfer which if not properly configured could cause the truck to easily flip over or slide out during a turn.
This effect is worsened when the truck is carrying heavy payloads as the weight from the payload will also move which can also shift the truck’s centre of gravity and can be very dangerous.
Most unmanned trucks won’t be built specifically for speed, instead, they’ll focus more on being made for maximum payload capacity and efficiency while still ensuring they are stable to maintain the integrity of the payload they’re transporting. A good balance between all of these factors is essential.
They also need power sources which are devices used to generate and provide power to the other components in the robot. Power sources include many devices such as a powered tether, engines, batteries, fuel cells, solar cells etc.
Check out our full post where we dive into several powerplants and propulsion devices used in drones. For each power source, we expand on how they work, the types, advantages/disadvantages, and examples of drones using it:
Related Post: How Are Drones Powered? 6 Drone Energy Sources Explained
Some can be electrically powered (electric trucks), some can be gas/petrol powered (engine-powered trucks), and some can also be hybrids incorporating both types of propulsion systems in a single vehicle just like in unmanned buses.
This is referring to the main source of power as many unmanned trucks with engines also have small batteries for example used to power other less critical internal components.
The braking systems used by unmanned trucks differ depending on whether they’re electric or mechanical.
In electric brakes, the electronic speed controller (ESC) controls this by locking the current flowing from the motors.
In mechanical brakes, brake disks attached to brake pads held together to the wheel by brake callipers apply resistance to the differential system thus slowing down the robotic truck.
There are two-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, six-wheel drive, eight-wheel drive, ten-wheel drive, twelve-wheel drive, and all-wheel drive unmanned trucks. This refers to which pair of drive wheels on a drive axle is powered in a truck.
They often require much larger wheels (sometimes even two tires on each side) on each axle as the payload they carry is in almost every case much higher than smaller unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) such as unmanned cars.
What Are The Types Of Unmanned Trucks?
The types of unmanned trucks can be split up according to:
- The general types
- The chassis types
- The truck bed designs/configurations
- The number of wheels
- The control system
The general types of unmanned trucks include unmanned pickup trucks, box trucks/vans, concrete mixer trucks, forklift trucks, refuse/garbage trucks, flatbed trucks, monster trucks, boom trucks, dump trucks/tippers, off-road trucks etc.
The chassis types of unmanned trucks include unmanned straight/conventional trucks (rigid) and tractor-trailers/semi-trucks (articulated).
The types of unmanned trucks according to the truck bed designs/configurations include unmanned open-bed trucks and closed-bed trucks.
The types of unmanned trucks according to the number of wheels include four-wheeled trucks, six-wheeled trucks, eight-wheeled trucks, ten-wheeled trucks, twelve-wheeled trucks, fourteen-wheeled trucks, sixteen-wheeled trucks, and eighteen-wheeled trucks.
The types of unmanned trucks according to the control system used include remote-controlled (RC)/teleoperated, semi-autonomous, fully autonomous, and hybrid control system trucks.
What Are Unmanned Trucks Used For?
Here are 5 applications for unmanned trucks:
- Freight/cargo delivery
- Garbage pickup and disposal
- Mixing concrete
- Enabling individuals to attain hard to reach areas at certain heights (mobile cranes)
- Transporting firefighters and water in emergency situations
What Parts/Components Make Up Unmanned Trucks?
The integrity of the cargo onboard the truck is the most important factor to take into account. The parts and components that make up these unmanned vehicles ensure that they achieve this task while operating on the road.
Here are 7 main parts & components that make up unmanned trucks:
- Structural system
- Body/shell
- Powertrain
- Steering system
- Communications system
- Braking system
- Automation system
The structural system is the strongest part of the UGV that supports all other components and payloads within the robot in order for it to function.
This can refer to the drone’s frame or chassis, or the combination of the frame with other components that enable the vehicle to move including the transmission, engine, steering etc which is then called a rolling chassis which simply requires a body/shell to be completed.
The two types of truck chassis include rigid chassis and flexible/articulated chassis.
Articulated trucks typically have a drawbar/tow bar in order to connect the tractor unit to the trailer.
The trailer in semi-trucks, also called tractor-trailers, is often a long enclosed separate compartment with its own set of wheels and stores the cargo.
The body/shell is the part of an unmanned truck that typically covers the chassis/frame protecting the internal components. It can come separate from the chassis/frame or come permanently attached to it (unibody chassis).
The body can be designed to replicate the design of almost any type of manned truck.
The cab is the enclosed box on the tractor unit where the driver sits and/or where the important internal components are stored and protected.
For ease of access to the trailer, some larger semi-trailers have tail lifts which are platforms that are permanently attached to the back door of a trailer and can lift and lower objects into the trailer.
The powertrain is the group of components that generate and transmit power to the drive axle/wheels. It includes the drivetrain and the propulsion system used by the robotic truck.
The steering system is the system that enables the entire robot to change direction according to the desired course of the drone and/or operator.
The communications system is the system enabling the operator to send and receive data to and from the unmanned truck. This can be used to monitor the sensors on the vehicle over long distances and/or to control the drone.
A radio transmitter and receiver are typically used to achieve this along with all other parts and components enabling the vehicle to be controlled.
The braking system is the system that enables a truck to brake. This can be achieved using brake discs (mechanical brakes) or an electronic speed controller (ESC) that locks or reverses the motor’s current (electric brakes).
The automation system is the group of components that enable an unmanned truck to function either semi-autonomously (little human intervention) or fully autonomously (no human intervention) using a group of components that all work together such as sensors and complex computer programs.
What Are The Advantages & Disadvantages Of Unmanned Trucks?
We’ve split up the advantages and disadvantages of unmanned trucks into separate sections.
Unmanned truck robot advantages
Here are 5 advantages of unmanned trucks:
- They are designed to transport large quantitites of payload at one time
- Fully autonomous trucks don’t get tired, lose focus, or need to stop for breaks
- They are often very strong and durable
- They can be made to be very versatile
- Their stability ensure the cargo/freight is kept safe and sustains no damage during transit
Unmanned truck robot disadvantages
Here are 5 disadvantages of unmanned trucks:
- They are often very large and heavy
- They are difficult to operate (especially large trucks)
- They are sometimes slow
- The laws on autonomous trucks on roads are currently very strict
- They are not very fuel-efficient
What Are Some Examples Of Unmanned Trucks?
Remote-controlled (RC) trucks have been around for a while now, but semi-autonomous trucks are still fairly new and fully autonomous vehicles are not yet truly operational due to restrictions in both the technology and the laws.
Some of these examples will include prototypes of autonomous trucks that have not yet been released or are just in the trial phases. For trucks that are meant to be fully autonomous, we will consider them fully/semi-autonomous vehicles.
Here are 7 examples of unmanned trucks:
| Name | Manufacturer | Chassis Type | Control System |
| Driverless Truck Unit | Uber (Otto) | Tractor-Trailer (Articulated) | Fully/Semi-Autonomous |
| Driverless Truck | TuSimple | Tractor-Trailer (Articulated) | Fully/Semi-Autonomous |
| Half-Pipe Tipper | ScaleArt | Straight Truck (Rigid) | Remotely-Controlled (RC) |
| Autonomous Box Trucks | Gatik | Straight Truck (Rigid) | Fully/Semi-Autonomous |
| Self-Driving Truck | Aurora | Tractor-Trailer (Articulated) | Fully/Semi-Autonomous |
| Mercedes-Benz Actros 3363 | Tamiya | Tractor-Trailer (Articulated) | Remotely-Controlled (RC) |
| 793D Haul Truck (Converted) | Ferrexpo | Straight Truck (Rigid) | Fully/Semi-Autonomous |
If you’d like to discover who the best drone companies are in the world for the consumer, commercial and military drone markets and some fun facts about them, we have a full post on this topic below:
Related Post: Top Drone Companies/Manufacturers In The World [History, What They Offer, Popular Drones And More]
Conclusion
Unmanned trucks, specifically autonomous trucks have been on the rise in recent years and for good reason. They can potentially revolutionise various industries such as construction, mining, and transportation.
We hope you’ve learned something new from this article and have broadened you’re understanding of these incredible unmanned vehicles.
