The amount of terminology and abbreviations used in the topic of unmanned vehicles is vast and can be overwhelming at first. This is why we have created this post which includes many common and some uncommon expressions with their definitions.
We’ve split this up into multiple sections according to several factors so that it’s easier to find specific terms that apply to specific categories within the drone niche. Here they are.
Drone terminology and abbreviations based on:
- General Terms and Abbreviations
- Operating Environment
- Size
- Design
- Powerplant
- Takeoff+Landing Method
- Range+Endurance
- Manufacturer+Regulatory Agency
- Components/Flight Mode
- Locomotion Mode
- Application/Target Market
- General Drone Terminology And Abbreviations
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Operating Environment
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Size
- Drone Terminology Based On Design
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Powerplant
- Drone Abbreviations Based On Takeoff+Landing Method
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Range+Endurance
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Manufacturer+Regulatory Agency
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Components+Flight Mode
- Drone Terminology Based On Locomotion Mode
- Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Function/Application
- Conclusion
General Drone Terminology And Abbreviations
The general drone terminology and abbreviations section refers to all terms and abbreviations that do not fit in the primary categories specified above.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| DRONE | Dynamic Remotely Operated Navigation Equipment | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated robot that is capable of sensing information, processing it, and executing a physical action that changes something in the world without a pilot on board |
| VLOS/LOS | Visual Line Of Sight/Line Of Sight | The drone’s pilot or visual observer maintains an unobstructed view of the drone from a maximum distance of 500 meters (1,640 feet) during flight |
| EVLOS | Extended Visual Line Of Sight | The drone’s pilot or visual observer maintains an unobstructed view of the drone from 500 meters (1,640 feet) and further during flight |
| BVLOS | Beyond Visual Line Of Sight | The drone’s pilot or visual observer has no visual reference of the drone during flight |
| RC | Radio/Remote Controlled | Method of wireless communication via remote controllers (transmitters) using radio waves |
| RPV | Remotely Piloted Vehicle | Any unmanned vehicle that can be operated remotely/wirelessly |
| ROV | Remotely Operated Vehicle | Any unmanned vehicle that can be piloted remotely/wirelessly |
| AGL | Above Ground Level | The altitude directly under a UAV. If the ground is elevated under the aircraft, the measurement will stop at the highest point of that elevation |
| MSL | Mean Sea Level | The average level of the surface of a sea/an ocean. This elevation will serve as the starting point when measuring a drone’s altitude |
| AMSL | Above Mean Sea Level | Refers to any altitude above MSL. This measurement is used when calculating the altitude of a UAV in reference to the MSL |
| BNF | Bind-N-Fly | A drone that is ready to be linked to a controller to be used straight out of the box with no additional setup steps |
| RTF | Ready-To-Fly | A drone that comes with every component needed straight out of the box |
| PNP | Plug-N-Play | A drone that comes with every component except for a transmitter, receiver, battery, and charger |
| ARF/ARTF | Almost-Ready-To-Fly | A drone that comes partially assembled and needs a few essential components before it can be used |
| FPV | First Person View | A popular method that uses an onboard video camera that is wirelessly connected to a pilot’s FPV goggles on the ground giving the impression that they’re in the drone’s cockpit |
| Drone FOV | Drone Field Of View | The maximum observable view of the world from the onboard camera of a drone |
| EMI/RFI | Electromagnetic Interference/Radio-Frequency Interference | Interference caused by an external source that interrupts and affects an electrical circuit |
We have a full post that explains what the differences are between drones, UAVs and UAS:
Related Post: What Is The Difference Between A Drone, UAV And UAS [Definitions, Differences In Cost, Examples And Acronyms]
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Robot | A mechanical robot is a device/machine with a body capable of physically changing something in the world around it. It senses information around it, processes that information, and then executes the best course of action |
| Unmanned System | Any electro-mechanical vehicle that does not have a pilot on board and can make a physical change in the world using its power. It can however transport passengers |
| Autonomous Drone | Any unmanned vehicle that requires minimal to no human intervention to function by utilising artificial intelligence. They can perceive their environments, process that data, and artificially think of the best course of action |
| Mobile Robot | Any machine capable of moving around its environment |
| Fixed Robot | Any machine which is anchored to a point and uses manipulators such as arms to perform tasks |
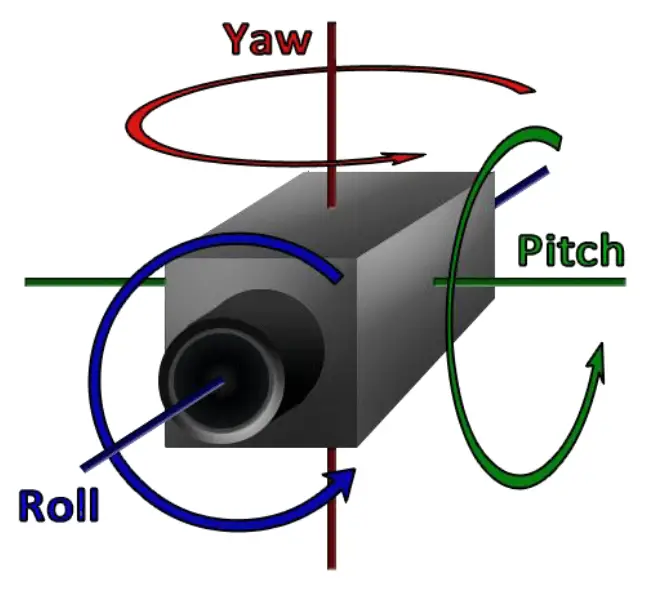
| Yaw/Normal Axis | The yaw axis is a movement of a vehicle from top to bottom. For aircraft, this would be parallel to the fuselage |
| Pitch/Transverse Axis | The pitch motion is a left to right motion from the front of a vehicle |
| Roll/Longitudinal Axis | The roll motion draws through the body of the vehicle from tail to nose in the normal direction of travel, or the direction front of the vehicle is facing |
| Drone Trim | The process of adjusting the yaw, pitch, roll, and throttle using the set buttons on a drone’s transmitter. This is essential when a drone is off balance or drifting |
| Bind | The process of linking a drone’s transmitter (controller) to the drone itself |
| Fail-Safe | Protocol ensuring a machine suffers minimal damage in the event of a breakdown or malfunction |
| Video Latency | The degree of delay between the time a transfer of a video stream is requested and the actual time that transfer begins |
| Thrust | Thrust is a force generated when a system pushes mass in one direction causing thrust (force) that is just as large to be pushed in the opposite direction |
| Drone Swarm | Group of drones flying in unison to complete a collective behaviour |
| Teleoperated Robot | Robots that are controlled remotely by a human being. The remote control signals can be transmitted through a wire (Drone Tether), through a wireless system (Wi-Fi), over the Internet or by satellite |
| Telepresence Robot | Type of teleoperated drone. The pilot operates the drone remotely but acts as though they see through the drone in first-person view (FPV) |
| Automated/Pre-Programmed Robots | Robots that are programmed to perform specific tasks, then execute that program. They cannot deviate from their programming and do not need any human intervention in most cases |
| Drone Flight Simulator | Software program made to simulate the experience of flying a drone using real drone controllers that are connected to a compatible device |
| Drone Course | Set of lessons covering specific or general topics related to drone technology |
Check out our post where we explain whether a drone is a robot, what a drone and a robot are, some types of robots, the difference between the two, and some examples of each:
Related Post: Is A Drone Considered A Robot? Everything You Need To Know
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Operating Environment
The operating environment section refers to the environment drones are used. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial/Air Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated in the air |
| UAS | Unmanned Aerial/Air System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned aircraft from the control station on the ground to the wires inside the UAV |
| AAV | Autonomous Aerial/Air Vehicle | Any autonomous mechanical robot that is operated in the air |
| AAS | Autonomous Aerial/Air System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned autonomous aircraft for it to function |
| UGV | Unmanned Ground Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated on land/the ground |
| UGS | Unmanned Ground System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned land vehicle from the transmitter to the vehicle itself |
| AGV | Autonomous Ground Vehicle | Any autonomous mechanical robot that is operated on land/the ground |
| AGS | Autonomous Ground System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned autonomous aircraft for it to function |
| USV | Unmanned Surface Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated on the surface of a body of water |
| USS | Unmanned Surface System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned surface vehicle from the transmitter to the vehicle itself |
| ASV | Autonomous Surface Vehicle | Any autonomous mechanical robot that is operated on the surface of a body of water |
| ASS | Autonomous Surface System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned autonomous surface system for it to function |
| UUV | Unmanned Undersea/Underwater Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated underwater |
| UUS | Unmanned Undersea/Underwater System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned underwater vehicle from the transmitter to the vehicle itself |
| AUV | Autonomous Undersea/Underwater Vehicle | Any autonomous mechanical robot that is operated underwater |
| AUS | Autonomous Undersea/Underwater System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned autonomous underwater system for it to function |
| CTA | Controlled Airspace | Controlled airspace is airspace of defined dimensions within which air traffic control (ATC) services are provided |
| UA | Unmanned Aircraft | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated in the air |
| RPA | Remotely Piloted Aircraft | Any aircraft that is piloted remotely using methods of wireless communication such as Wi-Fi or satellite transmission |
| RPAS | Remotely Piloted Aerial System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned aircraft for it to function |
| Underwater ROV | Underwater Remotely Operated Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated underwater |
| ROUV | Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated underwater |
| NFZ | No-Fly Zone | Restricted areas of set dimensions where aircraft cannot fly |
| FRZ | Flight Restriction/Restricted Zone | Restricted areas of set dimensions where aircraft cannot fly |
| AE | All Environment | Military designation indicating a system can be used in all environments |
If you’d like to find out how deep underwater ROVs can go, whether this is referring to consumer drones or professional drones not available to the general public, then check out our post on this topic here:
Related Post: How Deep Can Underwater Drones Go? Guide To ROV Depth Capabilities
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Underwater Drone | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated mechanical robot that is operated underwater |
| Unmanned Sailplane/Glider | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned aircraft that is designed to fly without the use of an engine (unpowered) |
| Unmanned Flying Boat | Any unmanned seaplane that takes off, lands and floats with its fuselage on water |
| Unmanned Aerostat | Lighter-than-air aircraft that gains lift through the use of a buoyant gas stored inside a non-rigid (Blimp), semi-rigid, or rigid gasbag often protected by an outer envelope |
| Unmanned Airship | Type of powered free-flying unmanned aerostat that can be steered |
| Unmanned Balloon | Type of unpowered free-flying or tethered unmanned aerostat that uses wind as means of propulsion. These can either be tethered or free-flying |
| Unmanned/Uncrewed Spacecraft | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated uncrewed mechanical robot that is operated in space |
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Size
The size section refers to the different sizes drones come in. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| MAV | Micro Air Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical aircraft that is extremely small and ultra-lightweight |
| NAV | Nano Air Vehicle | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical aircraft that is extremely small and ultra-lightweight |
| SUAV | Small Unmanned Aerial/Air Vehicle | Any small remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical aircraft that is small in size |
| SUAS | Small Unmanned Aerial/Air System | Refers to a small unmanned air vehicle and every component that makes up that aircraft and allows it to function |
Check out our post where we dive into whether the size of a drone matters, the differences between the two, the different drone sizes, some examples of both small and large drones, and more:
Related Post: Small VS Large Drones – Does The Size Of Your Drone Matter?
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Miniature Unmanned Air/Aerial Vehicle (UAV) | Any unmanned aircraft that is small enough to be man-portable |
| Nano Drone | Any unmanned mechanical vehicle similar in size to that of an insect. Often referred to as drones that weigh less than or equal to 250g (8.8oz) |
| Microdrone | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical vehicle that is extremely small and ultra-lightweight |
| Mini Drone | Any unmanned vehicle that is small enough to be man-portable |
| Nanocopter | Any mechanical rotorcraft similar in size to that of an insect |
| Tiny Whoop | Small first-person-view aircraft |
We have a full post on drone sizing where we go into not only the various sizes drones come in, but we also talk about whether the size of a drone matters, consumer, commercial and military drone sizes, how to measure the frame size of a drone and much more:
Related Post: Drone Sizes Explained: Consumer, Commercial And Military Drone Sizes
Drone Terminology Based On Design
The design section refers to every design drones come in. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Fixed-Wing Drone | Any unmanned aircraft that uses wings that stay in a fixed position to fly |
| Conventional Wing Drone | Any unmanned aircraft that has wings, a fuselage, and a tail |
| Flying Wing Drone | Any unmanned tailless aircraft with no distinct fuselage |
| Lifting Body Drone | Any unmanned aircraft or spacecraft with no distinct wings that relies on its fuselage for lift |
| Blended Wing-Body Drone | Any unmanned aircraft with no clear distinction between the wings and body of the drone |
| Single Rotor Helicopter Drone | Any unmanned rotorcraft that uses a single main rotor usually located above the body of the drone and an anti-torque device such as a tail-rotor located at the tail of the aircraft to fly |
| Multicopter | Any rotorcraft that uses two or more rotors to fly |
| Tricopter | Any rotorcraft that uses three rotors to fly |
| Quadcopter | Any rotorcraft that uses four rotors to fly |
| Hexacopter | Any rotorcraft that uses six rotors to fly |
| Octocopter | Any rotorcraft that uses eight rotors to fly |
| Bipedal Robot | Any mechanical robot that uses two legs to move around |
| Quadrupedal Robot | Any mechanical robot that uses four legs to move around |
| Hexapod | Any mechanical robot that uses six legs to move around |
| Eight-Legged Robot | Any mechanical robot that uses eight legs to move around |
| Unmanned Tracked Robot | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical ground system that uses which use treads or caterpillar tracks to move around |
| Unmanned Wheeled Robot | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical ground system that uses which use wheels to move around |
| Unmanned Legged Robot | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned mechanical ground system that uses which use legs to move around |
| Unmanned Non-Rigid Airship/Blimp | Unmanned airship without an internal structural framework or a keel |
| Unmanned Semi-Rigid Airship | Unmanned airship with a stiff keel supporting the main envelope along its length |
| Unmanned Rigid Airship | Unmanned airship in which the envelope is supported by an internal framework |
| Hybrid VTOL Drone | Hybrid between fixed-wing drones and rotorcraft that utilises both technologies in one system |
| Powered Lift Drone | Type of vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) drone that uses power to propel itself |
| Convertiplane | Type of powered lift VTOL drone that uses rotor power for vertical takeoff and landing and can transition to forward fixed-wing horizontal flight |
| Quadplane | Type of convertiplane that uses four rotors for vertical takeoff and landing and can transition to forward fixed-wing horizontal flight |
| Tiltrotor Drone | Type of convertiplane that uses rotors for vertical takeoff and landing which then tilt to propel the aircraft into forward horizontal flight with the help of fixed-wings |
| Tiltwing Drone | Type of convertiplane that uses rotors attached to a wing which is positioned vertically for vertical takeoff and landing and then tilt horizontally for forward horizontal flight |
| Tilting Ducted Fan Drone | Type of convertiplane that uses ducted fans for vertical takeoff and landing which then tilt to propel the aircraft into forward horizontal flight with the help of fixed-wings |
| Tail-Sitter Drone | Type of powered lift drone that takes off and lands on its tail then tilts horizontally for forward horizontal flight |
| Rotary-Wing Drone/Rotorcraft | Type of VTOL drone that uses one or more rotors which quickly rotate generating lift to fly |
| Unmanned/Uncrewed Spacecraft | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated robotic spacecraft |
| Robotic Spacecraft | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned spacecraft |
| Unmanned Resupply/Cargo Spacecraft | Type of unmanned spacecraft that is designed to carry and transport cargo from one place to another in space |
| Space Probe | Type of unmanned spacecraft that doesn’t orbit the Earth, instead exploring outer space beyond our planet to gather scientific research |
| Space Observatories | Type of unmanned spacecraft found in outer space used to observe distant planets, galaxies and other astronomical objects |
| Unmanned Ornithopters | Any remotely operated, autonomous, or automated unmanned drone that achieves flight by flapping its wings like a birds |
| Unmanned Gliders/Sailplanes | Unpowered unmanned fixed-wing aircraft that gains altitude by using naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere |
If you’d like to learn more on the different types of drones including the types according to design, payload, range, power source and use cases including some examples of both consumer, commercial and military drones, then check out our full post below:
Related Post: What Types Of Drones Are There? Every Type Of Drone Explained In Detail
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Powerplant
The powerplant section refers to every power source used to propel air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| LiPo | Lithium-Polymer (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte |
| Li-ion | Lithium-Ion (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions to function |
| LiHv | Lithium-Polymer High Voltage (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that provides higher voltage rates than LiPo batteries |
| Li-Air | Lithium-Air (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses oxidation of lithium at the anode and reduction of oxygen at the cathode to induce a current flow |
| NiCd | Nickel Cadmium (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes |
| NiMH | Nickel Metal Hydride (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses nickel oxide hydroxide at the positive electrode and a hydrogen-absorbing alloy at the negative electrodes |
| Pb-Acid | Lead-Acid (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that uses plates made of pure lead or lead oxide for the electrodes and sulfuric acid for the electrolyte |
| ZAB | Zinc-Air (Battery) | Type of rechargeable battery that is powered by oxidizing zinc with oxygen from the air |
| FC | Fuel Cell | Powerplant that uses the chemical energy of fuels such as hydrogen to produce electricity |
| PEMFC | Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell | Type of fuel cell that uses acidic polymer membrane as its electrolyte, with platinum-based electrodes |
| DMFC | Direct Methanol Fuel Cell | Type of PEMFC that uses methanol as fuel |
| SAFC | Solid Acid Fuel Cell | Type of fuel cell that uses a solid acid material as the electrolyte |
| SOFC | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell | Type of fuel cell where the electrolyte is a solid, nonporous metal oxide, typically zirconium oxide (ZrO2) treated with Y2O3, and O-2 is transported from the cathode to the anode |
| AFC | Alkaline Fuel Cell | Type of hydrogen/oxygen fuel cell in which the electrolyte is concentrated potassium hydroxide (KOH) and the hydroxide ions (OH–) are transported from the cathode to the anode |
| PV | Photovoltaics | The process of converting light into electricity using semiconducting materials |
| CNG | Compressed Natural Gas (Fuel) | Type of alternative fuel to gasoline primarily made of methane |
| TVC | Thrust Vector Control | Type of propulsion system used by aircraft or rockets to change the direction of thrust generated by their engines or motors |
Learn more on how long drone batteries last where we dive into the average flight times for both consumer and commercial drones, including the average drone battery life expectancies, the types of drone batteries, why drones have short flight times and battery life expectancies, how to increase both and more:
Related Post: How Long Does A Drone Battery Last? Battery Life Expectancy + Flight Times
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Gas/Combustion Turbine Engine | Type of internal combustion engine that burns an air-fuel mixture which produces hot gases that spin a turbine to produce power |
| Turbofan Engine | Type of airbreathing jet engine that uses a turbojet engine that drives a ducted fan to function |
| Turbojet Engine | Type of airbreathing jet engine that uses a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle to function |
| Turboprop Engine | Variant of turbojet engines where the gas turbine drives a propeller to generate thrust |
| Turboshaft Engine | Type of gas turbine engine that generates shaft power rather than jet thrust by adding turbine expansion which is used to pull heat from the exhaust to convert it into shaft power |
| Rotary Engine | Type of internal combustion engine that generates rotary motion or that has a rotating part or parts |
| Piston/Reciprocating Engine | Any engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion |
| Hybrid Engine | Any engine that combines two different energy sources |
| Solar Power System | Power source that converts the energy from sunlight into electricity. The two methods used are called photovoltaics (PV) and concentrated solar power |
| Drone Tether | Any drone that is attached using a physical link (Cable/flexible wire). This tether can provide power to the system, or be used as a means of communicating with it |
| Laser Power Beaming | The process of powering a drone with energy stored in lasers that travel from a ground station to a modified photovoltaic (PV) cell that is attached to the vehicle |
| Electricity (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source |
| Gasoline/Petrol (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source |
| Diesel (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source |
| Jet Fuel (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source used in jet engines |
| Nitromethane/Nitro Fuel (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source used most often in nitro engines |
| Hydrogen (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source commonly used in unmanned vehicles |
| Gas/Electric Hybrid (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source that utilises both gasoline and electricity |
| Ethanol (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source most often used as fuel for motors |
| Propane (Fuel) | Type of fuel/energy source |
| Unmanned Unpowered Aerostat | Any unmanned unpowered lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of buoyant gas stored in a gasbag |
| Unmanned Powered Aerostat | Any unmanned powered lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of buoyant gas stored in a gasbag |
| Entomopter | Type of ornithopter (wing-flapping drone) that uses artificial muscles to re-create the aerodynamics of an insect |
Check out our full post where we dive into several power sources currently used in drones. For each power source, we expand on how they work, the different types, the advantages, disadvantages, and real-world examples of drones that use it.
Related Post: How Are Drones Powered? 6 Drone Energy Sources Explained
Drone Abbreviations Based On Takeoff+Landing Method
The takeoff+landing method section refers to the methods in which drones take off and land. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| VTOL | Vertical Takeoff & Landing | Any drone that can both take off and land vertically |
| CTOL/HTOL | Conventional/Horizontal Takeoff & Landing | Any fixed-wing drone that takes off along a runway horizontally |
| STOL | Short Takeoff & Landing | Any drone that takes off along a shorter runway compared to conventional runway lengths |
| VTVL | Vertical Takeoff & Vertical Landing | Any rocket-powered drone that can both take off and land vertically |
| V/STOL | Vertical and/or Short Takeoff & Landing | Any drone that can take off and land both vertically or on short runways |
Check out our detailed post where we dive into how VTOL drones work, the types of VTOL drones according to flight modes, designs, and propulsion methods, their costs, how much they weigh, their payload capacities, use cases, examples, and more:
Related Post: What Are Vertical Takeoff And Landing (VTOL) Drones? (+hybrid variants)
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Range+Endurance
The range+endurance section refers to the distance and the maximum flight time of a drone. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| HALE | High-Altitude Long Endurance | Any aircraft that operates over 9,000m (29,528ft) |
| MALE | Medium-Altitude Long Endurance | Any aircraft that operates up to 9,000m (29,528ft) |
| EER | Extended Endurance & Range | Military designation used for a variant of the Lockheed Martin Desert Hawk |
Check out our post on military UAV flight range where we compare manned to unmanned military flight range, we talk about the factors that impact maximum flight range, and we take a look at some military UAVs with the longest range today:
Related Post: How Far Can Military Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) Fly?
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Hand-Held UAV | Any UAV that operates at 2,000 ft (600 m) altitude and around 2 km range |
| Close-Range UAV | Any UAV that operates at 5,000 ft (1,500 m) altitude and up to 50km |
| Short-Range UAV | Any UAV that operates between 51-160km |
| Mid-Range UAV | Any UAV that operates over 200km |
| Long-Range/Endurance UAV | A UAV with indefinite range |
Check out our post on military UAV flight speeds where we compare manned to unmanned military flight speeds, we talk about the factors that impact maximum flight speed, and we take a look at some of the fastest military UAVs today:
Related Post: How Fast Do Military Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) Fly?
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Manufacturer+Regulatory Agency
The manufacturer+regulatory agency section includes manufacturers that design and make drones and regulatory agencies that create and maintain aviation laws and regulations in every country.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition/Purpose |
| NAA/CAA | National Aviation Authority/Civil Aviation Authority | A NAA/CAA is a government authority that can be found in every country that regulates and approves civil aviation and an aircraft register |
| ICAO | International Civil Aviation Organization | An organization that’s funded and directed by 193 national governments to support their diplomacy and cooperation in air transport |
| EASA | European Aviation Safety Agency | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in the European Union (EU) |
| CAA | Civil Aviation Authority (United Kingdom) | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in the United Kingdom |
| FAA | Federal Aviation Association | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in the United States |
| DGCA | Directorate General for Civil Aviation | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in France |
| AESA | Aviation Safety and Security Agency | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in Spain |
| CASA | Civil Aviation Safety Authority | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in Australia |
| BCAA | Bermuda Civil Aviation Authority | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in Bermuda |
| OFAC (French) | Federal Office for Civil Aviation | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in Switzerland |
| PFCO | Permission For Commercial Operation | Refers to the document you need to operate a drone commercially in United Kingdom airspace |
| LAANC | Low Altitude Authorization and Notification Capability System | It provides access for drone pilots to controlled airspace around 731 airports in the United States |
| DoD | Department of Defense | American government agency that provides the US military forces needed to deter war and ensure security |
| COA | Certificate Of Authorization | Refers to the document granted to a drone pilot or organization to conduct a specific type of activity |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration | U.S. government agency that is responsible for science and technology related to air and space |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization | Organization that creates and introduces worldwide standards |
| DJI | Da-Jiang Innovations | Chinese drone manufacturing company that designs drone hardware, software and accessories |
| DMI | Doosan Mobility Innovations | South Korean drone manufacturing company |
| IE | Intelligent Energy | Company providing drone components and powerplants |
| GA | General Atomics | American energy and defence corporation that specializes in research and technology development |
| LMC | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Global security and aerospace company engaged in research, design, development, manufacturing, integration and sustainment of advanced technology systems, products and services |
Check out our post where we dive into whether or not you can take your drone on a plane. We include the TSA rules on drones, whether drone batteries are allowed, whether you can take it on both carry-on and checked luggage, countries that have banned drones and some safety tips and tricks when travelling with a drone:
Related Post: Are Drones Allowed On Planes? Essential Drone Travel Tips
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Part 107 | Refers to the certificate you need to operate a drone commercially in United States airspace |
| Transport Canada Civil Aviation Directorate | Refers to a NAA that is located and run in Canada |
| PowerLight Technologies | Company that specialises in laser power beaming technology |
| Parrot | French drone manufacturing company |
| Yuneec | Chinese drone manufacturing company that designs drone hardware and accessories |
| 3D Robotics | American drone manufacturing company that designs drone hardware and software |
| Autel Robotics | American drone manufacturing company that designs drone hardware |
| Boeing | American aerospace manufacturing company that designs all sorts of aircraft including drones through its subsidiary Insitu |
| BAE Systems | British company that develops, delivers and supports advanced defence and aerospace systems |
If you’d like to discover more about who the best drone companies are in the world for the consumer, commercial and military drone markets and some fun facts about them, we have a full post on this topic below:
Related Post: Top Drone Companies/Manufacturers In The World [History, What They Offer, Popular Drones And More]
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Components+Flight Mode
The components+flight mode section refers to every part that makes up an unmanned system from the physical drone itself and what it’s made up of to the control station used to control it and the different features drones have. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
We have a full post that goes into detail about each component used in drones and their materials (including some examples of drones and their materials):
Related Post: What Are Drones Made Of? Detailed Guide To Drone Anatomy [Consumer+Commercial]
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| FLIR | Forward Looking InfraRed Camera | An electro-optical thermal imaging device that detects far-infrared energy and converts the energy into an electronic signal |
| TX | Radio Transmitter | Equipment that generates and transmits electromagnetic waves to the receiver |
| RX | Radio Receiver | Equipment that converts electromagnetic waves into visible signals |
| GCS | Ground Control Station | Land or sea-based hardware and software that allows drone operators to communicate with and control a drone and its payloads |
| MCS | Mobile Control Station | Mobile hardware and software that allows drone operators to communicate with and control a drone and its payloads |
| IOC | Intelligent Orientation Control | Allows you to change the forward flying direction of a UAV according to the controls regardless of the direction the nose of the aircraft facing |
| ESC | Electronic Speed Controller | Device used in drones to control and change the speed of their electric motors. |
| BEC | Battery Eliminator Circuit | Device used to evenly distribute power to every electric component that needs power in a drone therefore eliminating the need for multiple batteries |
| PDB | Power Distribution Board | Component in drones that distributes power to each electronic speed controller |
| SATCOM | Satellite Communications | System that includes constellations of Earth-orbiting satellites that broadcast their locations in space and time, of networks of ground control stations, and of receivers that calculate ground positions by trilateration |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System | System that includes constellations of Earth-orbiting satellites that broadcast their locations in space and time, of networks of ground control stations, and of receivers that calculate ground positions by trilateration |
| GPS | Global Positioning System | United States global navigation satellite system that synchronizes the location, velocity and time of a drone |
| GLONASS | GLObal NAvigation Satellite System | Russian Federation’s global navigation satellite system that synchronizes the location, velocity and time of a drone |
| GIS | Geographic Information System | System capable of capturing, storing, analysing, managing and presenting data about location |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit | Electronic device that measures and reports a body’s specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers |
| INS | Inertial Navigation System | Self-contained navigation device consisting of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and computational unit that continuously calculates the position, orientation, and velocity of a moving object |
| ACAS | Autonomous Collision Avoidance System | Safety system designed to prevent or decrease the severity of a collision before it occurs by autonomously taking over the controls and attempting to alter its course |
| OSD | On-Screen Display | Control panel on a monitor or screen that provides viewing and adjustment options of the display, such as brightness, contrast, and horizontal/vertical positioning |
| OAS/OCAS | Obstacle (Collision) Avoidance System | Safety system designed to prevent or decrease the severity of a collision before it occurs by alerting the operator before it occurs |
| CAS | Collision Avoidance System | Safety system designed to prevent or decrease the severity of a collision before it occurs by alerting the operator before it occurs |
| RTH/RTL | Return To Home/Return To Launch | Feature found in some drones that allows it to automatically return to its starting position where it took off |
| FC | Flight Controller | Drone circuit board equipped with varying numbers of sensors that process the information gathered by the sensors and controls things such as the speed of the aircraft. It is considered the brain of the drone |
| Lidar | Light Detection and Ranging | Method of using a pulsed laser to measure distances by calculating the time it takes for a laser that is pointed at an object to return to the receiver |
| FRP | Fibre-Reinforced Plastic | Composite material that’s made of a polymer matrix and is reinforced with fibres |
| PP | Polypropylene | Thermoplastic polymer made from the monomer propylene |
| TPU | Thermoplastic Polyurethane | Thermoplastic elastomer |
| EPO | Expanded Polyolefin | Moulded plastic foam material |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene | Thermoplastic and amorphous polymer |
| VRX | Video Receiver | Equipment that converts electromagnetic waves (video in this case) into visible signals |
| VTX | Video Transmitter | Equipment that generates and transmits electromagnetic waves (video in this case) to the receiver |
| SIGINT | Signal Intelligence | Intelligence-gathering by interception of signals |
| COMINT | Communication Intelligence | Type of SIGINT where the signals are communications between people |
| ELINT | Electronic Intelligence | Type of SIGINT where the signals are electronic and are not directly used in communication |
| EO | Electro-Optical Systems | Imaging systems that utilise a combination of electronics and optics to generate, detect, and/or measure radiation in the optical spectrum |
| IR Camera | Infrared/Thermographic Camera | Device that creates images using infrared radiation |
| IP Rating | Ingress Protection Rating | Defines the sealing effectiveness of electrical enclosures against water, dirt, dust, moisture etc |
We highly recommend you check out our full detailed post on drone propellers including the different types, how they work, their different sizes and pitch, their materials, how to choose them and much more.
Related Post: Drone Propellers Explained: Detailed Beginner’s Guide To Drone Anatomy
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Drone Fuselage | Main body of a drone where payloads and cargo are stored |
| Propeller Guard | Drone safety device that comfortably fits around the propellers of underwater, surface and aerial unmanned vehicles to protect them from obstacles |
| Prop/Propeller | Device used for propulsion in unmanned fixed-wing, rotorcraft, underwater and surface vehicles by quickly rotating |
| Deep-Cycle | Type of battery capable of being nearly completely discharged (drained of energy) and recharged regularly significantly increasing its life expectancy |
| Firmware | Specific type of software that adds some control for a device’s specific hardware |
| Drone Software | Programs and information that instruct a drone system on what to do |
| Drone Hardware | Every physical component that makes up a drone such as its wiring, powerplant, fuselage etc |
| Accelerometer | Sensor used to measure the acceleration of motion of a drone |
| Actuator | Component that is responsible for moving and controlling a machine |
| Robotic Manipulator | Device used by robotic systems to manipulate/move objects and materials around them. These are most often referred to as robotic arms |
| Geofencing | Feature found in some drones that warns or restricts a drone from entering specific areas based on its GPS |
| Drone Gimbal | Device used in drones to support a camera while keeping it steady and allowing it to smoothly rotate around one or more axes |
| Data Link | Telecommunications link from a transmitter to a receiver that transmits digital information |
| Ocusync | Wireless transmission system that transmits data from one point to another |
| Wi-Fi | One of the most widely used wireless transmission systems that transmits data from one point to another |
| Telemetry System | Automatic measurement and wireless transmission of data from remote sources |
| Payload | Additional weight added to the drone’s base weight (empty weight) which includes equipment such as cameras, gimbals, and sensors |
| Gyroscope | Instrument that measures the rate of rotation of a drone ensuring the vehicle stays balanced with respect to yaw, pitch and roll |
| Normal/Standard Mode | Mode that places the controls relative to the cockpit/front of the drone |
| Sport Mode | Mode found in DJI UAVs that maximises the sensitivity of its yaw, pitch, roll via the throttle removing some of the drone’s restrictions, in turn reducing operating time |
| Manual Mode | Mode that completely removes most if not all restrictions that assist drone operators while using the vehicle |
| Headless Mode | Mode that places the controls relative to the direction of the operator. If the pilot pushes forward on their controller, the drone will move away from the operator no matter the orientation of the vehicle |
| Active Track | Mode that enables a UAV to simultaneously track a specific object while recording it even if it is in motion |
| Gesture Mode | Mode that enables an operator to control a UAV by making simple hand and arm movements |
| Cinematic Mode | Mode found in DJI UAVs that reduces the maximum rotation speed of its motors providing smoother images and reduces the yaw speed of the aircraft |
| Tapfly Mode | Mode found in DJI UAVs that keeps the drone flying in the same direction with the click of a button until it is deactivated |
| Self-Level Mode | Mode that enables a drone to automatically level itself back off after the operator releases the forward position on the stick |
| Brushless Motor | Component found in every unmanned rotorcraft that uses a temporary brushless electromagnet (stator) alongside a rotor, as a means of converting electrical energy into kinetic energy |
| Brushed Motor | Component found in every unmanned rotorcraft that uses a permanent brushed electromagnet (stator) alongside a rotor, as a means of converting electrical energy into kinetic energy |
| Throttle | Component that controls the speed or flow of fuel of an engine or the amount of power applied to an electric vehicle |
| Ultrasonic Sensor | Device that measures the distance and detects the presence of an object by producing and measuring an ultrasonic echo |
| Topographic Lidar | Type of light detection and ranging (lidar) that typically uses a near-infrared laser to map the land |
| Bathymetric Lidar | Type of light detection and ranging (lidar) that uses water-penetrating green light to also measure seafloor and riverbed elevations |
| Thermoplastics | Type of plastic polymer material that becomes soft when heated and hard when cooled (curing) |
| Thermosets/Thermosetting Polymers | Type of plastic polymer material that becomes irreversibly hard when heated (curing) |
| Fibreglass | Type of fibre-reinforced plastic using glass fibre often used in high-end drones |
| Carbon Fibre | Material made of carbon atoms often used in drones due to its strength, low weight, high-temperature tolerance and low thermal expansion |
| Composite Materials | Any material made using two or more constituent materials |
| Tailplane | The small horizontal wing found on the tail of fixed-wing drones and also on some rotorcraft |
| Proprotor | Any rotating airfoil that acts as both an aeroplane propeller and a helicopter rotor providing both vertical and horizontal propulsion. Commonly found on tiltrotor and tiltwing aircraft |
If you’d like to find out what a drone gimbal is, what kinds of drone gimbals are available, whether drones need gimbals, how a drone gimbal works, how to choose the right gimbal, how much they cost and much more, check out our post on this topic below:
Related Post: What Is A Drone Gimbal? Does Your Drone Need One? [Types, How They Work, Prices And How To Choose One]
Drone Terminology Based On Locomotion Mode
The locomotion mode section refers to the method which robots use to transport themselves from one place to another. This includes air, ground, surface of a body of water, and underwater drones.
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Walking Robot | Any robot that uses leg actuators to walk |
| Rolling Robot | Any robot that can roll using either a spherical body, wheels, tracks etc |
| Hopping Robot | Any robot that can hop or jump around. These robots are typically legged |
| Slithering Robot | Any robot that can slither like a snake as a means of locomotion |
| Flying Robot | Any robot that flies. This includes rotorcraft and winged aircraft |
| Swimming Robot | Any robot that can operate underwater or on the surface of a body of water |
| Brachiating Robot | Any robot that travels by swinging. This includes continuous contact where the component that grabs the object is continuously attached to it and ricochetal where the robot swings from one object to another with a brief period of flight in between the two objects |
Drone Terminology And Abbreviations Based On Function/Application
The application/target market section includes the tasks the robot was made to be able to accomplish and the market or industry it was built for.
Abbreviations:
| Shortened | Full | Definition |
| UCAV | Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle | Any unmanned aerial vehicle that is used for combat. This typically includes intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR) applications |
| UCAS | Unmanned Combat Aerial System | Refers to every component that makes up an unmanned aerial vehicle that is used for combat. This typically includes intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR) applications |
| GEOINT | Geospatial Intelligence | The analysis of information gathered from images and data associated with a particular location |
| IMINT | Imagery Intelligence | The analysis of information gathered from images to gather intelligence |
| MASINT | Measurement And Signature Intelligence | Type of intelligence gathering that detects, tracks, identifies or describes the distinctive characteristics of fixed or dynamic targets |
| ISR | Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance | The process of acquiring, processing, and providing accurate, relevant, and timely information using optical, radar, infrared images, and electronic signals |
| ISTAR | Intelligence, Surveillance, Target Acquisition and Reconnaissance | The process of acquiring, processing, and providing accurate, relevant, and timely information using optical, radar, infrared images, and electronic signals |
| ISRT | Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance and Targeting | The process of acquiring, processing, and providing accurate, relevant, and timely information using optical, radar, infrared images, and electronic signals |
| TA | Target Acquisition | The process of acquiring, processing, and providing accurate, relevant, and timely information regarding the location of a target using optical, radar, infrared images, and electronic signals |
| IEW | Intelligence/Electronic Warfare | Detects, interprets, controls or disrupts signals in the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum, typically radar, radio or infrared transmissions, to protect military assets from potential threats |
Check out our post where we dive into the operating altitudes military UAVs can attain. We also dive into the factors that impact this maximum achievable altitude, and some examples of UAVs and their flight altitudes.
Related Post: At What Altitude Do Military Drones Fly? (+11 Examples)
Terminology:
| Term | Definition |
| Passenger Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed to transport passengers with at least a basic level of autonomy |
| Delivery Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed to transport cargo. These vehicles generally contain some form of autonomy |
| Aerial Photography | The process of taking photographs from any aerial vehicle |
| Autonomous Drone | Any device that carries out tasks with little to no human intervention |
| Semi-Autonomous Drone | Any device that carries out tasks with only a small amount of human intervention |
| Fully Autonomous Drones | Any device that carries out tasks without the need for any human intervention |
| Intelligence Gathering Drone | Any unmanned vehicle that is designed to gather some form of intelligence |
| Consumer/Recreational Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for hobbyists or the general public who intend on using it for fun |
| Domestic Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for hobbyists or the general public who intend on using it for fun |
| Commercial Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for individuals or organisations who intend on using it to make a profit in any way |
| Institutional Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used in a law, rule, or social practice that regulates an area of activity where many individuals engage such as law enforcement, education, or public service |
| Industrial Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used for manufacturing that’s capable of moving on three or more axes |
| Military Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used to attack, search and rescue, or transportation in the military |
| Toy/Consumer Grade | Any device designed for the general public/hobbyists to be used for fun |
| Trick Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for the general public/hobbyists to be used for fun that is capable of performing tricks such as backflips |
| Racing Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for the general public/hobbyists to be used for fun or professional racing |
| Camera Drone | Any unmanned vehicle designed for the general public to be used for fun or professional photography/videography |
| Drone Visual Photogrammetry | The art, science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through processes of recording measuring and interpreting images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant energy and other phenomena using unmanned vehicles |
| Drone Surveying | The process of examining an area and the features of a specific piece of land to build a map, plan, or detailed description using an unmanned vehicle |
| Drone 3D Modeling | The process of capturing images with unmanned vehicles and using special software that turns these images into digital spatial models |
| Search and Rescue Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used by emergency services such as firefighters or law enforcement ideal for searching and rescuing missing or injured individuals |
| Police Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used by law enforcement to locate missing or injured individuals or to locate fugitives |
| Research Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used to conduct tests and gather data in order to prove a theory |
| Demonstrator Drone | Any prototype unmanned vehicle built to prove a theory or concept and operated in controlled or uncontrolled environments |
| Experimental Drone | Type of research drone designed to test specific technologies and designs |
| Educational Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used by educational institutions to motivate and inspire students while simultaneously teaching them technological concepts |
| Scientific Drone | Any unmanned vehicle used for science-related applications |
| Surgical Drone | Any unmanned vehicle that is used in minimally invasive surgeries due to its capability of precisely manipulating surgical instruments beyond the capabilities of a surgeon |
| Social Drone | Any unmanned vehicle that interacts and communicates with people while following typical social behaviours |
Check out our post that dives into several applications that drones have today:
Related Post: 10 Common Uses of Drones In Our Daily Lives You May Not Know About
Conclusion
We hope you found the term/s you were looking for and understood its/their definition/s.
If you feel we’ve missed an important expression tied to the field of drones, feel free to contact me (the author) via email at aurelien@thecoronawire.com and we’ll add it as soon as possible!
Some of the definitions in this post were discovered from reliable sources provided below.
Sources:
- Lithium-air battery – Wikipedia
- Definition: Lead-acid battery | Open Energy Information
- Glossary | Department of Energy
- Gas Turbines for Power Generation – Introduction (wartsila.com)
- Reciprocating engine – Wikipedia
- About ICAO
- What is the Permission for Commercial Operation? (PfCO) | Drone Course & Drone Hardware (uavhub.com)
- What Is NASA? | NASA
- How Lockheed Martin Makes Money: Aeronautics, Missiles and Fire Control, Rotary and Mission Systems, and Space (investopedia.com)
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems: Educational curriculum (esa.int)
- Inertial measurement unit – Wikipedia
- Electro-Optical Systems | EO System Suppliers for UAV UGV Robotics (unmannedsystemstechnology.com)
- What is telemetry? – Definition from WhatIs.com (techtarget.com)
- What is lidar? (noaa.gov)
- Electronic Warfare | Thales Group
- What is ASPRS? – ASPRS