Unmanned cars, also called car unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) or robotic cars/automobiles have been around for a very long time. There are various types of unmanned cars that can further be split up into more categories which we’ll be diving into in this article.
The types of unmanned car drones/UGVs can be split up according to:
- The general types (Economy, sports, off-road, etc.)
- The body style/design (hatchback, sedan, roadster etc.)
- The number of wheels (Three-wheeled, four-wheeled, six-wheeled etc.)
- The control system (RC, Autonomous)
Robotic cars range in size from small toy-grade cars you can pick up to large scale manned cars that have been converted into unmanned vehicles.
Take note that unmanned cars include remote control (RC)/teleoperated, autonomous/self-driving, and artificially intelligent unmanned cars.
These types of unmanned vehicles fall under the broad category of unmanned motor vehicles. Unmanned motor vehicles are sub-types of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs).
A Quick Overview On What Unmanned Car Drones/UGVs Are And How They Work
Unmanned car drones have several systems enabling them to produce thrust and power.
They use various parts and components that work together enabling the vehicle to drive such as wheels, a chassis, suspension systems, propulsion systems etc.
Check out our full post on the main parts/components of unmanned cars where for each part/component, we dive into what it is and how it works in further detail:
Related Post: Main Unmanned Car Robot/UGV Parts & Components Explained
Car UGVs experience several forces including thrust generated by a power source that opposes drag caused by air resistance and friction generated by the spinning wheels against the axles.
Pitch, roll, and yaw are each present in a moving robotic car and can be controlled to a degree by the suspension system.
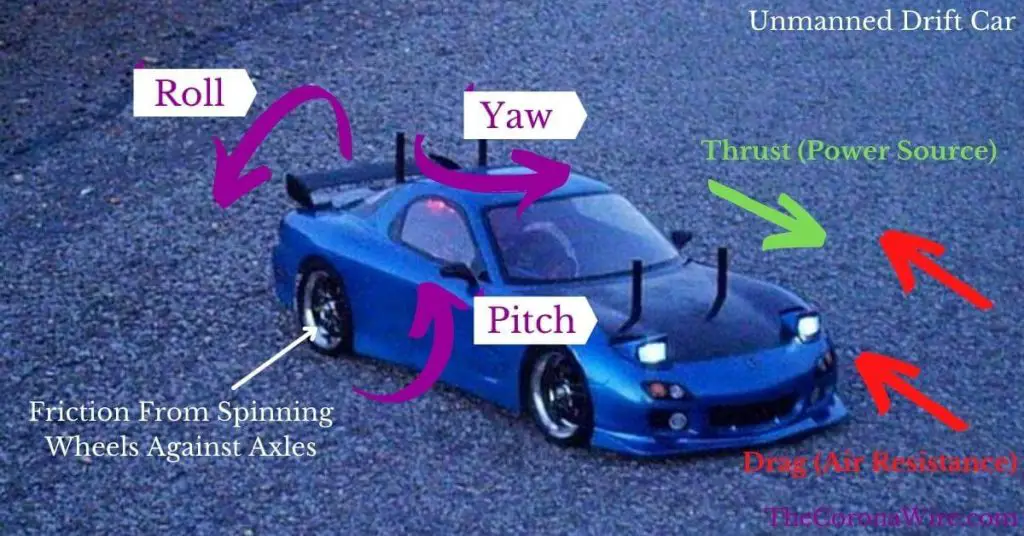
The entire body of the car is also designed in a way that reduces aerodynamic drag caused by air resistance while still being durable and capable of containing important internal components.
They also need power sources which are devices used to generate and provide power to the other components in the robot. Power sources include many devices such as a powered tether, engines, batteries etc.
These types of robots are either electric unmanned cars or are powered by an internal combustion engine using either gasoline or nitro fuel.
This is referring to the main source of power as many unmanned cars with engines also have small batteries used to power other components.
There are two-wheel drive (most common), four-wheel drive (often found in off-road cars), eight-wheel drive (rare), and all-wheel drive unmanned cars. This refers to which pair of wheels on a drive axle is powered in a car. Each of these are types of drivetrain configurations.
Check out our full post on what unmanned cars are where we dive further into how they work, their applications, parts/components, advantages/disadvantages, propulsion systems they use and examples:
Related Post: What Are Unmanned Cars? Drone/UGV Automobiles Explained
General Types Of Unmanned Cars
This section includes all the general types of car drones/unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) that make up a large part of these types of robots.
Here are the 5 general types of unmanned cars:
- Economy cars
- Sports cars
- Off-road cars
- Luxury cars
- Custom cars
These general types of unmanned cars are very broad classes of UGVs that can technically include every type of robotic car as long as it meets the requirements from each definition.
Unmanned economy cars
Unmanned economy cars are small low-cost compact unmanned cars designed to focus on interior space and fuel economy.

Generally, economy cars like most cars use different body styles/designs including the hatchback, station wagon/estate, sedan/saloon, and coupé body configurations (more on this in the next section).
These types of cars are primarily used to transport passengers or lightweight cargo.
Check out our full post on unmanned car applications. For each application, we dive into what it is, how it works, and some examples if any:
Related Post: 6 Awesome Unmanned Car Robot/UGV Applications Explained
They’re generally much cheaper than other types of unmanned cars and focus on the basic features most people look for in a vehicle such as space and efficiency.
The Fiat 500X made by RW (seen in the image above) and the Mini Cooper S made by Rastar Group which are both RC cars are two examples of unmanned economy cars.
Unmanned sports cars
Unmanned sports cars are typically small compact unmanned cars that are designed to focus on performance such as handling, top speed, and acceleration.

The types of unmanned sports cars include unmanned touring cars, drift cars, muscle cars, go-karts, formula one cars, dragsters, grand tourers (GTs), supercars, rally cars, and NASCAR stock cars.
These types of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) are going to be built to either transport people if large enough or can be equipped with sensory payloads in order to be driven remotely and potentially in first-person view (FPV).
Unmanned sports cars are built for speed and handling and will therefore benefit from the thrill of driving at high speed. However, this massive increase in speed can be more dangerous and less comfortable specifically for passenger-carrying unmanned cars.
The Ford GT made by Traxxas (seen in the image above) which is an RC unmanned grand tourer (GT) and the Quicksilver gas dragster made by Primal RC which is a radio-controlled unmanned dragster are two examples of unmanned sports cars.
Unmanned off-road cars
Unmanned off-road cars are unmanned cars that are designed to be driven off-road (paved/gravel surfaces). These robotic cars can be large or compact and are often four-wheel drive with large wheels designed for off-road driving or tracks.
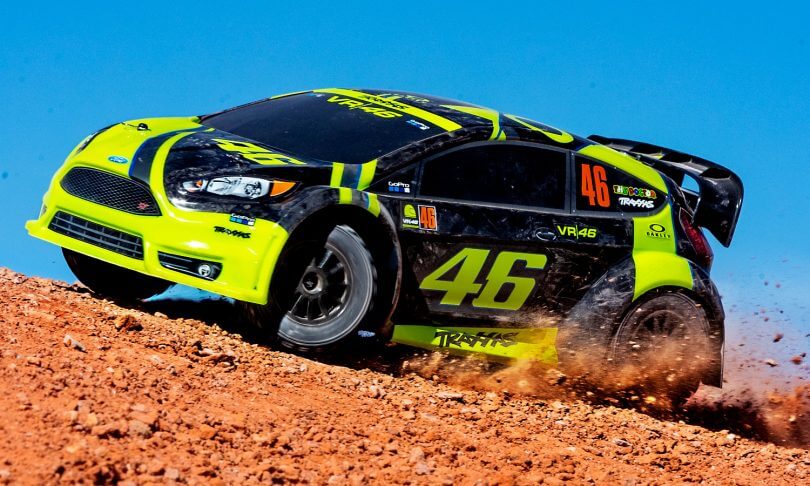

The types of unmanned off-road cars include rally cars (also considered sports cars) and sports utility vehicles (SUVs).
The primary advantage of these types of drones is obviously their incredible performance while driving off roads. However, they are not as suited for on-road driving.
The Ford Fiesta ST Rally (Valentino Rossi special edition) made by Traxxas (seen in the above image) which is an unmanned rally car and the Halo Project made by the Mississippi State University (MSU) which is an autonomous sports utility vehicle (SUV) are two examples of unmanned off-road cars.
Unmanned luxury cars
Unmanned luxury cars are unmanned cars that are designed to provide more features such as comfort and performance for a higher price than other types of unmanned vehicles.
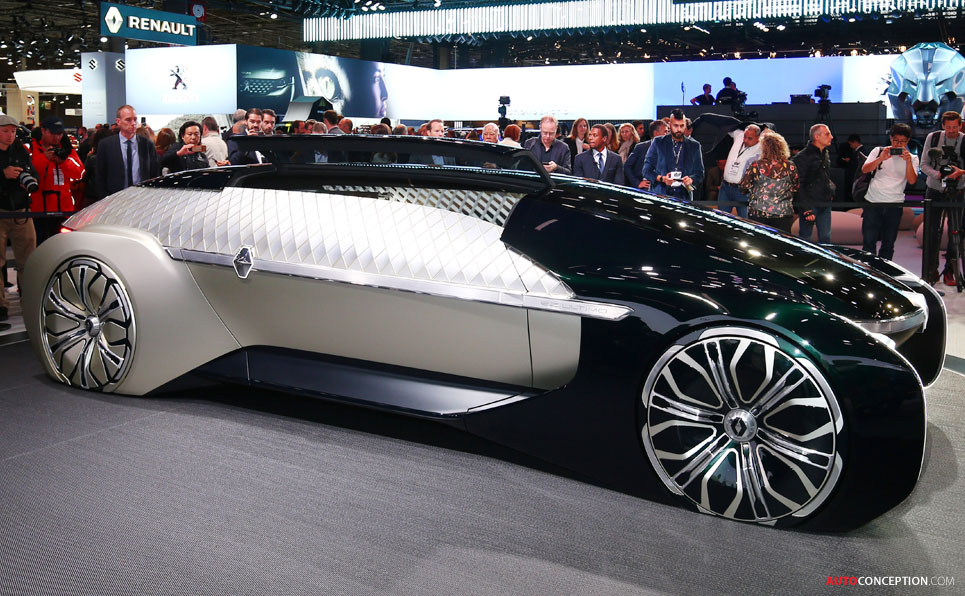

Unmanned limousines and supercars are specific types of unmanned luxury cars. However, any type of robotic car that meets the above requirements can be considered a luxury car.
These can be small radio-controlled cars that have been equipped with upgraded equipment increasing their performance and the quality of the materials they’re made of or large autonomous vehicles with similar upgrades.
The look of the vehicle, especially if modelled after a manned vehicle from an expensive brand, can contribute to the decision to classify it as an unmanned luxury vehicle.
Unmanned luxury passenger cars are going to provide more comfort for the passenger and more features making the trip more enjoyable and for those controlled remotely will benefit the operator with increased handling.
The EZ-ULTIMO concept autonomous limousine designed by Renault (seen in the image above) and the Corvette Stingray made by Traxxas which is an unmanned supercar are two examples of unmanned luxury cars.
Unmanned custom cars
Unmanned custom cars are heavily modified unmanned cars that have either upgraded or modified performance, body styles, and other features or combinations of all of these.
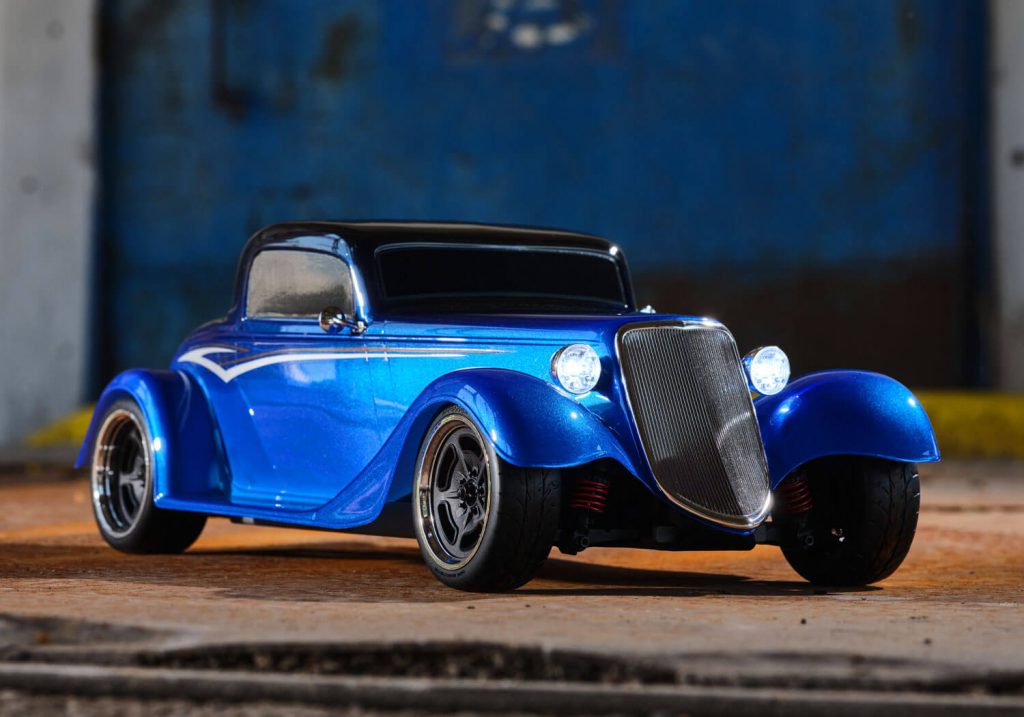

The types of unmanned custom cars include unmanned hi-risers/donks, lowriders, and hot rods.
These types of unmanned vehicles have the advantage of reusing a unique, maybe old, car body style and upgrading the performance and other features for a better experience.
However, these types of unmanned cars are often quite expensive depending on how modified they are and the car that their bodies and potentially interiors are based on (if any).
The 1933 Hot Rod coupe made by Traxxas (seen in the image above) which is an unmanned hot rod and the Hi-Riserz 1987 Buick Regal made by Motor Max which is an RC unmanned hi-riser/donk.
Types Of Unmanned Cars According To The Body Design/Configuration
These types of unmanned cars focus primarily on some specific features each have. These can be used for almost any type of unmanned car such as in unmanned sports cars, off-road cars etc.
Here are the 6 types of unmanned cars according to the body design/configuration:
- Hatchbacks
- Station wagons/estates
- Sedans/saloons
- Coupés
- Roadsters
- Convertibles/cabriolets
Unmanned hatchbacks
Unmanned hatchbacks are unmanned cars with rear doors (hatches/tailgates) which includes the rear window that typically swings upwards hinged at the car’s roof level.
They follow a two-box design configuration where the cargo area blends into the passenger area along with the second box being the power source area at the front of the car.
These types of cars differ from unmanned sedans/saloons as a sedan’s trunk lid is hinged below the rear window and therefore provides a much smaller opening.
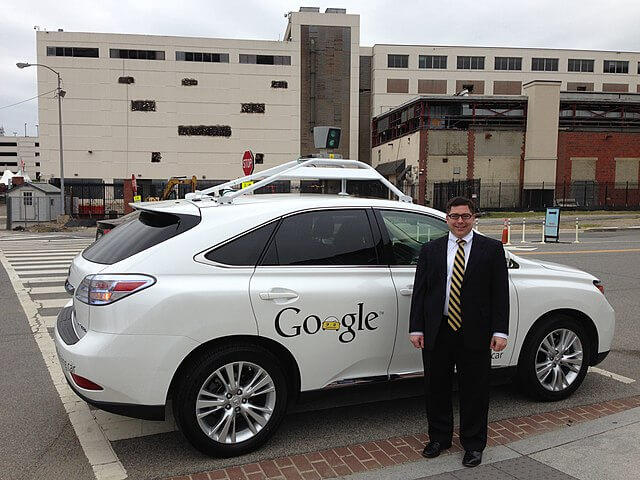

The types of unmanned hatchbacks can be split up based on the number of rows of seats they have (two-three rows), the tailgate/hatch configuration used (split-gate, side hinge, lift-gate etc.), and the number of doors they have (three-five door).
These types of vehicles have increased rear space where cargo is typically stored allowing people to store more cargo than other types of cars.
Google’s early prototype of their autonomous car (seen in the above image) before becoming Waymo used a modified Lexus RX450h which was a hatchback SUV.
Unmanned station wagons/estates
Unmanned station wagons/estates are unmanned cars that have a rear door/tailgate and have extended roofs giving them increased space for passengers or cargo.
They follow a two-box design configuration where the cargo area blends into the passenger area along with the second box being the power source area at the front of the car.
These types of robotic cars differ from unmanned hatchbacks as they are often longer and can feature an additional row of seats (three rows instead of just two like hatchbacks.
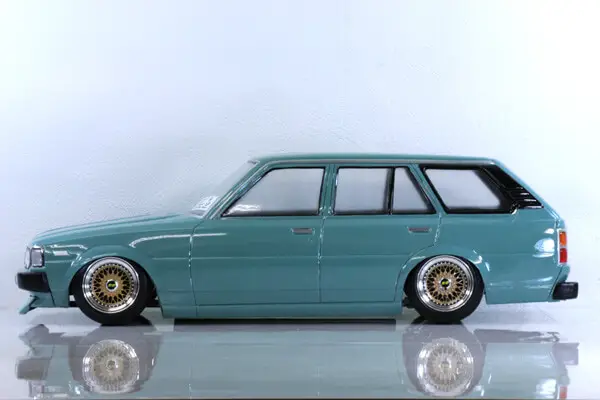

The types of unmanned station wagons/estates can be split up based on the number of rows of seats they have (two-three rows) and the tailgate configuration used (split-gate, side hinge, lift-gate etc.).
These types of drones can provide an increased amount of space for both cargo and passengers at a relatively low cost but lack performance and typically are not very visually pleasing.
The Toyota Corolla Wagon KE70 body made by Pandora RC (seen in the image above) and the 1963 Olds Station Wagon built by SuperScale with an incredible integrated active suspension system are two examples of unmanned station wagons.
Unmanned sedans/saloons
Unmanned sedans/saloons are types of unmanned cars that follow a three-box configuration where the power source (front), passenger, and cargo (rear) areas are separate. They typically have fixed roofs.
They differ from coupés as they have higher rooflines providing a little more room in the rear compartment and they have less of a sport-like look.
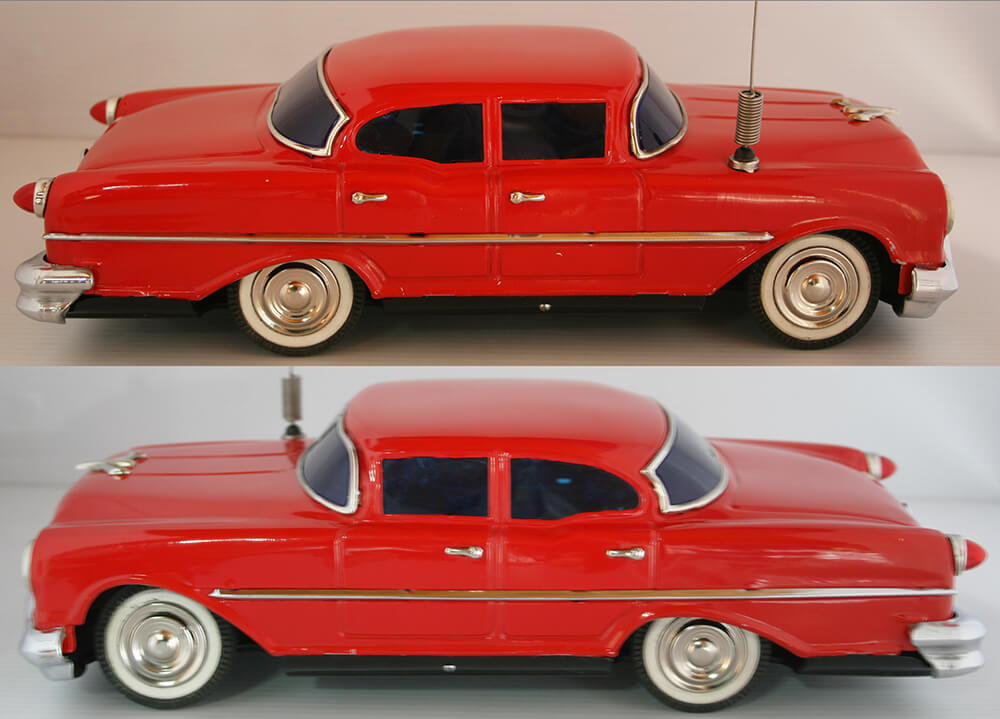

The types of unmanned sedans/saloons can be split up in various ways.
This includes the general types (hatchback/liftback, fastback, notchback, hardtop sedans), the number of rows of seats they have (one-two rows), and the number of doors they have (two-five doors including hatch if present).
These types of unmanned cars are very popular due to their balance in space, comfort, and efficiency.
The Radicon New Sedan made by Masudaya (seen in the image above) and the BMW E36 Sedan body sold by Aplastics are two examples of unmanned sedans/saloons.
Unmanned coupés
Unmanned coupés are types of unmanned cars that have fixed roofs and less headspace for passengers in the backseat if there are any as the roofline is sloped at the rear. They either have one or two rows of seats.
They’re typically more compact and have more sport-like car features compared to unmanned sedans/saloons.
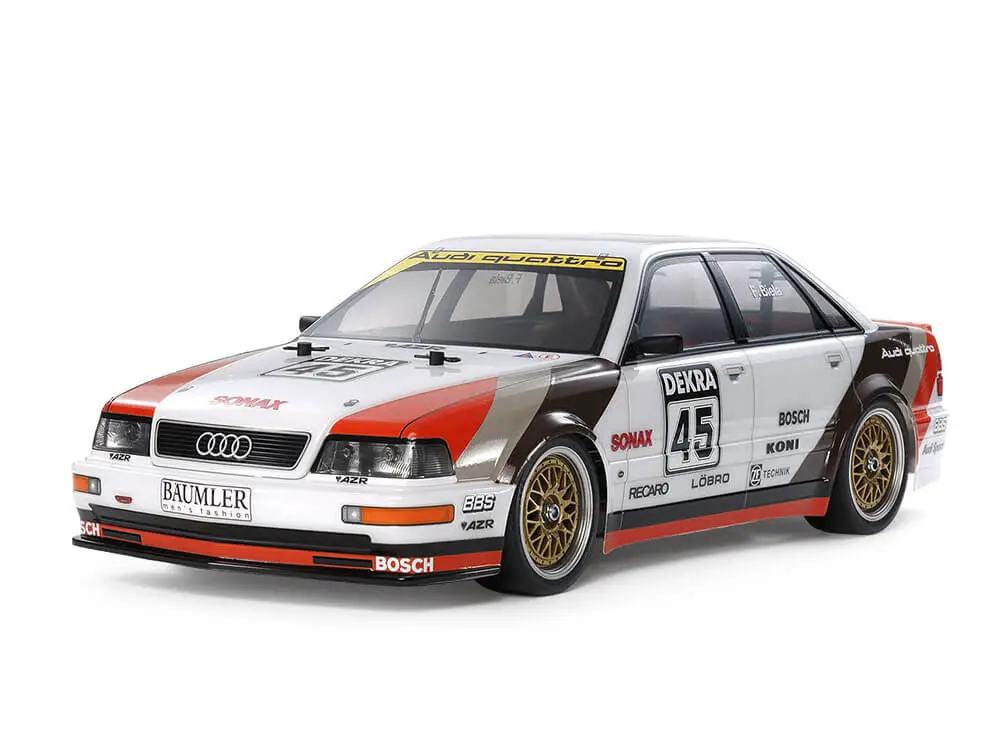

The types of unmanned coupés include berlinetta (sport), hardtop, and three-door coupés.
Unmanned coupés have the primary advantage of looks with a cut sport-like car body. However, these types of robotic cars do not have as much room as other types of cars.
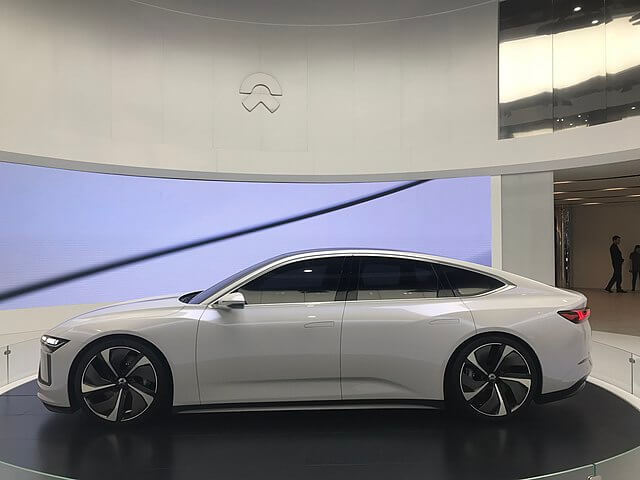
The Audi V8 touring car (TT-02) made by Tamiya Corporation which is an RC car (seen in the image above) and the NIO ET5 made by NIO which is an autonomous car are two examples of unmanned coupés.
Unmanned roadsters
Unmanned roadsters are open top (no fixed roof) unmanned cars with two seats designed to resemble a sports car.
These types of unmanned cars can have features found in convertibles.
These differ from robotic touring cars as touring cars require at least four seats.

Two-seat convertibles with no roof can also be considered roadsters as long as they’re built to resemble a sports car.
These types of unmanned vehicles are typically built for appearances but are not useful if the intention is to transport large quantities of payloads such as additional people (more than two) or cargo.
The BMW i8 Roadster made by Rastar Group (seen in the image above) and the BMW Z4 New Version also made by Rastar Group are two examples of roadsters that are controlled remotely.
Unmanned convertibles/cabriolets
Unmanned convertibles/cabriolets are unmanned cars that can be driven with or without a roof that can be made of fabrics, metal, or plastic.
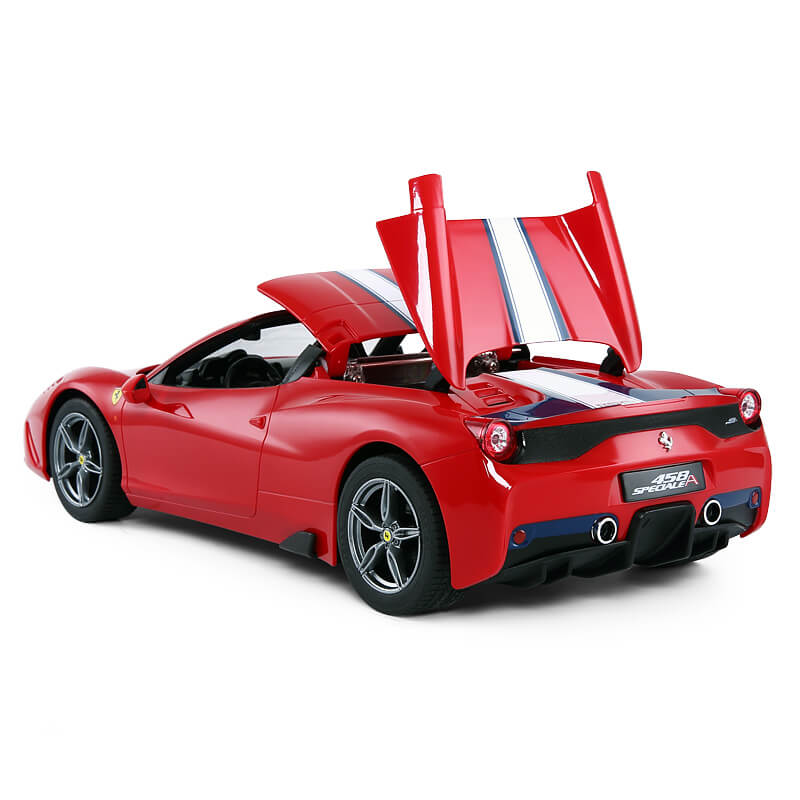

The types of unmanned convertibles can be split up according to the roof types they use. These include soft tops, retractable hardtops, and detachable hardtops.
Unmanned convertibles provide an open-air driving experience while still providing the same benefits as a fixed roof car.
However, they’re typically less structurally sound due to the system enabling their roofs to be removed.
The Ferrari 458 Speciale convertible version made by Rastar Group (seen in the image above) and the Bugatti convertible manufactured at Shenzhen Mingshun Technology are two examples of RC convertibles.
Types Of Unmanned Cars According To The Number Of Wheels
Robotic cars can be equipped with different numbers of wheels with four wheels of course being the most common.
Here are the 4 types of unmanned cars according to the number of wheels:
- Three-wheeled unmanned cars
- Four-wheeled unmanned cars
- Six-wheeled unmanned cars
- Eight-wheeled unmanned cars
Three-wheeled unmanned cars
Three-wheeled unmanned cars, also called unmanned three-wheelers, are powered unmanned cars that have three wheels with either two front wheels with one at the rear or vice versa.
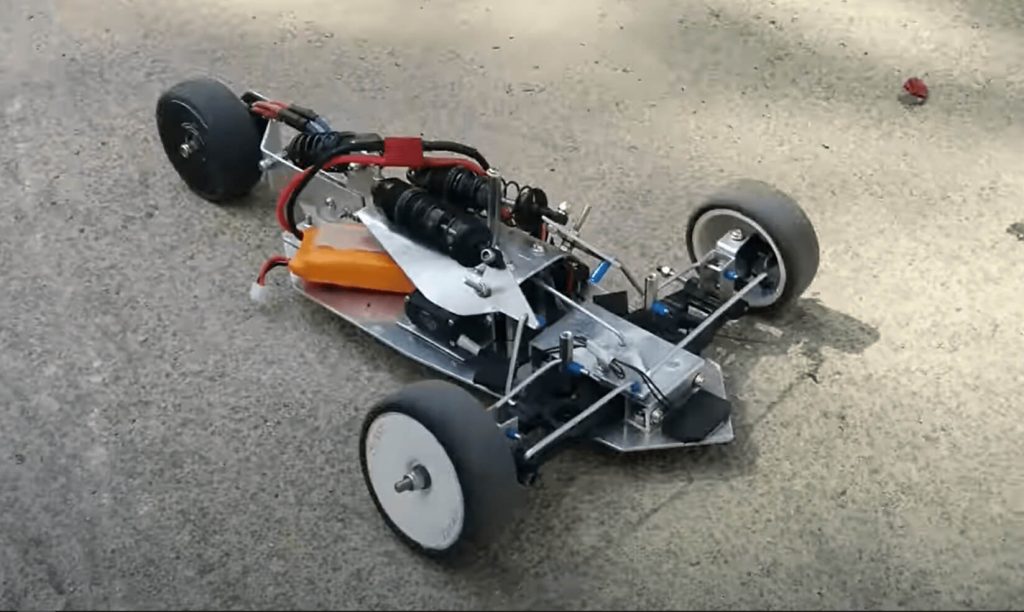

Unmanned three-wheelers are typically smaller than conventional vehicles but are not as stable, especially at higher speeds.
Three-wheelers that can tilt are commonly referred to as tilting three-wheelers.
These a fairly uncommon and are typically difficult to differentiate between a motorcycle (often motorised tricycle) and a car. The difference however is that motorised trikes are going to have the same control system used in conventional two-wheeled motorcycles.
Most unmanned three-wheelers have been built by enthusiasts as custom RC cars often by modifying the chassis of an existing vehicle.
Four-wheeled unmanned cars
Four-wheeled unmanned cars are powered unmanned cars with four wheels where each pair is placed on a separate axle.

These are the most common types of unmanned cars as they are simply the most all-around stable providing good handling over most other cars with more or fewer wheels.
These types of unmanned cars can either have two powered wheels generating thrust (two-wheel drive/2WD), or all four wheels doing so (four-wheel drive/4WD). If the car has four wheels and they’re all powered, this can also just be called all-wheel drive (AWD).
The NIO ET7 made by NIO which is an autonomous car and the 1969 Chevy Camaro made by Losi which is an RC AWD car are two examples of unmanned cars with four wheels.
Six-wheeled unmanned cars
Six-wheeled unmanned cars are powered unmanned cars with six wheels where each pair is placed on a separate axle.
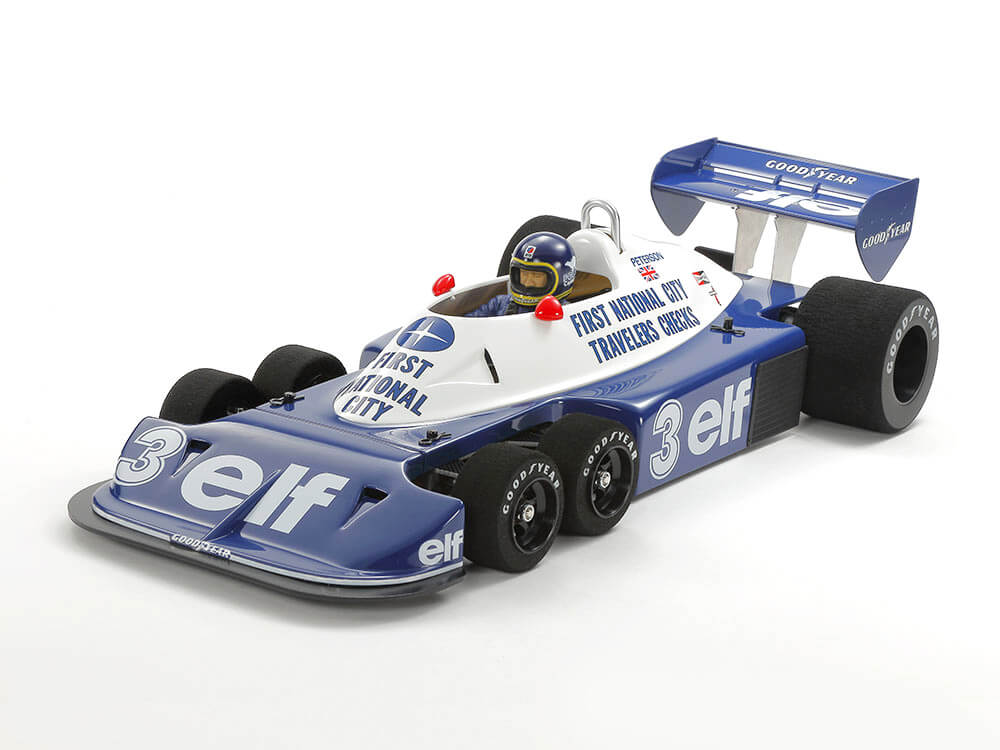

Six-wheeled vehicles are going to be capable of increasing the vehicle’s traction which is very beneficial off-road but is going to drastically increase the weight and therefore speed of the drone as well.
These types of unmanned vehicles can have either have four wheels generating thrust (four-wheel drive/4WD), or all six wheels (6WD/6×6). If all of their wheels are powered then they can also simply be referred to as all-wheel drive (AWD).
The Tyrrell P34 made by Tamiya Corporation (seen in the image above) which is an unmanned formula one RC car is an example of a six-wheeled unmanned car.
Eight-wheeled unmanned cars
Eight-wheeled unmanned cars are powered unmanned cars with eight wheels where each pair is placed on a separate axle.
These types of unmanned cars are very uncommon. They are much more common on truck chassis.
Types Of Unmanned Cars According To The Control System
Here are the 3 types of unmanned cars according to the control system:
- Remote controlled (RC)/teleoperated unmanned cars
- Autonomous unmanned cars
- Hybrid control system unmanned cars
Remote controlled (RC)/teleoperated unmanned cars
Remote-controlled (RC)/teleoperated unmanned cars are unmanned cars that are controlled remotely. This can be achieved using a transmitter typically in the form of a hand-held controller.

Hand-held controllers can come in two separate configurations. One being the pistol grip radio transmitter and the other being the stick radio transmitter.
There are also drones that can be controlled via a smartphone using wifi.
Radio communication is very reliable and enables an operator to have full control over their RC cars. However, they often have a limited range limiting the distance they can drive their cars.
Autonomous unmanned cars
Autonomous unmanned cars, also called driverless cars or self-driving cars, are types of unmanned cars that can sense their environments and can either follow a pre-programmed action or can make their own decisions depending on if they’re artificially intelligent.

There are two classes of autonomy.
One being semi-autonomous robots that can either follow a pre-programmed route or can utilise machine learning technology for brief periods of time while still requiring a human operator to take over from time to time.
Semi-autonomous robots are typically used to carry out repeatable tasks that are fairly simple to carry out.
And the second being fully autonomous robots that almost always have machine learning technology that do not ever require a human operator to take over.
In theory, unmanned cars with AI can revolutionise the automotive industry as they never get tired or lose focus (unless they run out of power of course).
However, machine learning technology enabling these types of vehicles to function fully autonomously is not yet at the level required to be capable of being fully integrated on real roads with other drivers.
The biggest issue is the unpredictability of other real drivers on the road.
Hybrid control system unmanned cars
Hybrid control system unmanned cars are unmanned cars that can alternate between several different control systems.
If one may fail or if the operator decides they want to switch for some reason, this becomes possible. This provides much wider flexibility which can be essential depending on how the robot will be used.
Conclusion
Unmanned cars cover a very large class of unmanned vehicles (specifically drones). These types of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) have revolutionised various industries and are continuing to do so as time goes on.
We hope you discovered a type of car drone you were not familiar with and understood how it works.
We highly recommend you check out our main article on what unmanned cars are and how they work.
